版权归作者所有,如有转发,请注明文章出处:https://cyrus-studio.github.io/blog/
现有脱壳方法存在的问题
脱壳粒度集中在 DexFile 整体,当前对 apk 保护的粒度在函数粒度,这就导致了脱壳与加固的不对等,无法应对函数粒度的加固保护。
Dalvik 下的基于主动调用的自动化脱壳方案,首次将粒度下降到函数粒度
-
https://github.com/zyq8709/DexHunter
-
https://github.com/F8LEFT/FUPK3
存在问题:
1、Dalvik 慢慢淡出视野,无法应对 ART 环境
2、当前没有一个好的脱壳修复框架,无法应用到 VMP 函数的修复
主动调用相关概念
1、被动调用
指 app 正常运行过程中发生的调用,该过程只对 dex 中部分的类完成了加载,同时也只是对 dex 中的部分函数完成了调用。
2、主动调用
通过构造虚拟调用,从而达到欺骗 “壳” ,让壳误以为 app 在执行正常的函数调用流程从而达成对 dex 中所有类函数的虚拟调用。
被动调用也可以用来完成函数粒度的修复。如当前通过正常运行 app ,待 app 将 dex 中的类正常加载并完成相关的函数的正常调用后再进行 dex 的 dump 的脱壳方法。
被动调用脱壳的缺点: 存在修复函数不全的问题。由于测试用例无法覆盖 dex 中所有的函数,导致代码覆盖率低,只能对 app 运行过程中调用过的函数的修复。
主动调用的优点: 能够覆盖 dex 中所有的函数,从而完成更彻底的函数粒度的修复。同时,函数的修复准确度同主动调用链的构造深度有关。
FART 中要解决的三个问题
1、如何构造主动调用链并让每一个函数都到达主动调用过程,但是又不影响 app 的正常运行?
2、如何根据 ArtMethod 定位内存中对应的 CodeItem 的起始地址?
3、如何遍历 dex 中的所有函数并完成主动调用?
如何构造主动调用链?
标准 Java 函数调用示例代码:
// 1. 查找 Java 类
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("com/cyrus/example/jniexample/JNIExample");
if (clazz == nullptr) {LOGI("Class not found");return env->NewStringUTF("Class not found");
}// 2. 获取 Java 方法 ID
jmethodID methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, "helloFromJava", "()Ljava/lang/String;");
if (methodId == nullptr) {LOGI("Method not found");return env->NewStringUTF("Method not found");
}// 3. 调用 Java 方法
jstring resultStr = (jstring) env->CallStaticObjectMethod(clazz, methodId);
标准流程:
-
通过 FindClass 得到 jclass
-
通过 GetStaticMethodID / GetMethodId 得到 jmethodID
-
通过一系列 Call 开头的函数完成调用(比如这里的 CallStaticObjectMethod)
FindClass
FindClass 的作用: 通过 ClassLinker 的 FindClass 取得目标类的 jclass
static jclass FindClass(JNIEnv* env, const char* name) {CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(name);Runtime* runtime = Runtime::Current();ClassLinker* class_linker = runtime->GetClassLinker();std::string descriptor(NormalizeJniClassDescriptor(name));ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);ObjPtr<mirror::Class> c = nullptr;if (runtime->IsStarted()) {StackHandleScope<1> hs(soa.Self());Handle<mirror::ClassLoader> class_loader(hs.NewHandle(GetClassLoader(soa)));c = class_linker->FindClass(soa.Self(), descriptor.c_str(), class_loader);} else {c = class_linker->FindSystemClass(soa.Self(), descriptor.c_str());}return soa.AddLocalReference<jclass>(c);}
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/jni/jni_internal.cc;l=654
GetMethodID / GetStaticMethodID 的作用:根据 jclass 对象、方法名和签名信息取得对应的 ArtMethod 用于下一步的调用
static jmethodID GetMethodID(JNIEnv* env, jclass java_class, const char* name, const char* sig) {CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(java_class);CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(name);CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(sig);ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);return FindMethodID(soa, java_class, name, sig, false);}static jmethodID GetStaticMethodID(JNIEnv* env, jclass java_class, const char* name,const char* sig) {CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(java_class);CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(name);CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(sig);ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);return FindMethodID(soa, java_class, name, sig, true);}
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/jni/jni_internal.cc;l=980
FindMethodID
GetStaticMethodID 和 GetMethodID 最终都是走到 FindMethodID ,只是传参 is_static 不同
static jmethodID FindMethodID(ScopedObjectAccess& soa, jclass jni_class,const char* name, const char* sig, bool is_static)REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {ObjPtr<mirror::Class> c = EnsureInitialized(soa.Self(), soa.Decode<mirror::Class>(jni_class));if (c == nullptr) {return nullptr;}ArtMethod* method = nullptr;auto pointer_size = Runtime::Current()->GetClassLinker()->GetImagePointerSize();if (c->IsInterface()) {method = c->FindInterfaceMethod(name, sig, pointer_size);} else {method = c->FindClassMethod(name, sig, pointer_size);}if (method != nullptr && ShouldDenyAccessToMember(method, soa.Self())) {method = nullptr;}if (method == nullptr || method->IsStatic() != is_static) {ThrowNoSuchMethodError(soa, c, name, sig, is_static ? "static" : "non-static");return nullptr;}return jni::EncodeArtMethod(method);
}
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/jni/jni_internal.cc;l=430
最后返回的是 jni::EncodeArtMethod(method),这是 ART 中将 ArtMethod* 转换为 jmethodID 的封装过程。
ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline jmethodID EncodeArtMethod(ArtMethod* art_method) {return reinterpret_cast<jmethodID>(art_method);
}
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/jni/jni_internal.h;l=55
jmethodID 在 ART 中其实就是一个 ArtMethod*,而 EncodeArtMethod 就是把 ArtMethod* 安全地封装成 jmethodID。
CallObjectMethod
CallObjectMethod / CallStaticObjectMethod 函数源码如下:
static jobject CallObjectMethod(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jmethodID mid, ...) {va_list ap;va_start(ap, mid);ScopedVAArgs free_args_later(&ap);CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(obj);CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(mid);ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);JValue result(InvokeVirtualOrInterfaceWithVarArgs(soa, obj, mid, ap));return soa.AddLocalReference<jobject>(result.GetL());}static jobject CallStaticObjectMethod(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jmethodID mid, ...) {va_list ap;va_start(ap, mid);ScopedVAArgs free_args_later(&ap);CHECK_NON_NULL_ARGUMENT(mid);ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);JValue result(InvokeWithVarArgs(soa, nullptr, mid, ap));jobject local_result = soa.AddLocalReference<jobject>(result.GetL());return local_result;}
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/jni/jni_internal.cc;l=997
InvokeVirtualOrInterfaceWithVarArgs 与 InvokeWithVarArgs
JValue InvokeVirtualOrInterfaceWithVarArgs(const ScopedObjectAccessAlreadyRunnable& soa,jobject obj, jmethodID mid, va_list args) {// We want to make sure that the stack is not within a small distance from the// protected region in case we are calling into a leaf function whose stack// check has been elided.if (UNLIKELY(__builtin_frame_address(0) < soa.Self()->GetStackEnd())) {ThrowStackOverflowError(soa.Self());return JValue();}ObjPtr<mirror::Object> receiver = soa.Decode<mirror::Object>(obj);ArtMethod* method = FindVirtualMethod(receiver, jni::DecodeArtMethod(mid));bool is_string_init = method->GetDeclaringClass()->IsStringClass() && method->IsConstructor();if (is_string_init) {// Replace calls to String.<init> with equivalent StringFactory call.method = WellKnownClasses::StringInitToStringFactory(method);receiver = nullptr;}uint32_t shorty_len = 0;const char* shorty =method->GetInterfaceMethodIfProxy(kRuntimePointerSize)->GetShorty(&shorty_len);JValue result;ArgArray arg_array(shorty, shorty_len);arg_array.BuildArgArrayFromVarArgs(soa, receiver, args);InvokeWithArgArray(soa, method, &arg_array, &result, shorty);if (is_string_init) {// For string init, remap original receiver to StringFactory result.UpdateReference(soa.Self(), obj, result.GetL());}return result;
}JValue InvokeWithVarArgs(const ScopedObjectAccessAlreadyRunnable& soa, jobject obj, jmethodID mid,va_list args)REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {// We want to make sure that the stack is not within a small distance from the// protected region in case we are calling into a leaf function whose stack// check has been elided.if (UNLIKELY(__builtin_frame_address(0) < soa.Self()->GetStackEnd())) {ThrowStackOverflowError(soa.Self());return JValue();}ArtMethod* method = jni::DecodeArtMethod(mid);bool is_string_init = method->GetDeclaringClass()->IsStringClass() && method->IsConstructor();if (is_string_init) {// Replace calls to String.<init> with equivalent StringFactory call.method = WellKnownClasses::StringInitToStringFactory(method);}ObjPtr<mirror::Object> receiver = method->IsStatic() ? nullptr : soa.Decode<mirror::Object>(obj);uint32_t shorty_len = 0;const char* shorty =method->GetInterfaceMethodIfProxy(kRuntimePointerSize)->GetShorty(&shorty_len);JValue result;ArgArray arg_array(shorty, shorty_len);arg_array.BuildArgArrayFromVarArgs(soa, receiver, args);InvokeWithArgArray(soa, method, &arg_array, &result, shorty);if (is_string_init) {// For string init, remap original receiver to StringFactory result.UpdateReference(soa.Self(), obj, result.GetL());}return result;
}
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/reflection.cc;l=616
所以,无论是静态方法还是非静态方法最终都会调用到 InvokeWithArgArray
void InvokeWithArgArray(const ScopedObjectAccessAlreadyRunnable& soa,ArtMethod* method, ArgArray* arg_array, JValue* result,const char* shorty)REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {uint32_t* args = arg_array->GetArray();if (UNLIKELY(soa.Env()->IsCheckJniEnabled())) {CheckMethodArguments(soa.Vm(), method->GetInterfaceMethodIfProxy(kRuntimePointerSize), args);}method->Invoke(soa.Self(), args, arg_array->GetNumBytes(), result, shorty);
}
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/reflection.cc;l=450
结论:对于 Java 函数的调用,最终由该函数对应的 ArtMethod 对象的 Invoke 函数完成。
如何 dump CodeItem?
dumpMethodCode
DexFIle 类添加 native 函数 dumpMethodCode,用于提取指定 ArtMethod 对应的 Dex 字节码(CodeItem)。
static void DexFile_dumpMethodCode(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jobject method) {// 将当前线程从 kNative 状态切换到 kRunnable,表示线程可以安全访问 Java 对象(如 jobject)。ScopedFastNativeObjectAccess soa(env);// 如果 Java 传入的 Method 不为 nullif(method != nullptr){// 将 java.lang.reflect.Method 转换为 ART 内部的 ArtMethod 指针ArtMethod* artmethod = ArtMethod::FromReflectedMethod(soa, method);// 调用 myfartInvokemyfartInvoke(artmethod);}return;
}
libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/DexFile.java
public final class DexFile {private static native void dumpMethodCode(Object m);
}
myfartInvoke 方法中主动调用 ArtMethod 的 Invoke 方法
extern "C" void myfartInvoke(ArtMethod * artmethod) SHARED_LOCKS_REQUIRED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {JValue *result = nullptr;Thread *self = nullptr;uint32_t temp = 6;uint32_t *args = &temp;uint32_t args_size = 6;artmethod->Invoke(self, args, args_size, result, "fart");
}
在 ArtMethod::Invoke 方法中,检测到 self 是 nullptr,也就是 myfartInvoke 的主动调用时,调用 dumpArtMethod 把解密后的函数 dump 下来
void ArtMethod::Invoke(Thread * self, uint32_t * args, uint32_t args_size, JValue * result,const char *shorty) {if (self == nullptr) {dumpArtMethod(this);return;}...
}
art/runtime/art_method.cc
获取 CodeItem 起始地址
CodeItem 起始地址就在 ArtMethod 的 dex_code_item_offset_ 字段。
不同 Android 版本略有不同

https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/art_method.h;l=755
通过 GetCodeItemOffset() 方法拿到 CodeItem 的起始地址

https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/runtime/art_method.h;l=378
CodeItem 结构定义
Android 源码中 CodeItem 的结构定义如下:
struct CodeItem : public dex::CodeItem {// DEX 字节码必须按照 4 字节对齐static constexpr size_t kAlignment = 4;private:// 方法使用的虚拟寄存器数量(包括本地变量和参数)uint16_t registers_size_;// 方法的入参占用的寄存器数量uint16_t ins_size_;// 方法调用其他方法时所需的最大出参寄存器数量(即调用其他方法时的参数空间)uint16_t outs_size_;// try-catch 块的数量。如果不为 0,则在 insns_ 后紧跟 try_item 和 catch_handler。uint16_t tries_size_;// 调试信息在 DEX 文件中的偏移,指向 debug_info 结构// 包括局部变量名、源码行号映射等uint32_t debug_info_off_;// 指令(insns_)数组长度,单位是 2 字节(code units)// 每条指令通常是 2 字节对齐,有些指令占用多个 code unituint32_t insns_size_in_code_units_;// 指令数组(实际大小是可变的,柔性数组)// 存放 DEX 字节码指令,insns_size_in_code_units_ 表示其长度uint16_t insns_[1];
};
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/libdexfile/dex/standard_dex_file.h;l=35
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/libdexfile/dex/compact_dex_file.h;l=87
CodeItem 前 16 字节是固定结构
| 字节偏移 | 字段名 | 含义说明 | 大小(字节) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | registers_size_ | 方法使用的寄存器数(本地变量 + 参数) | 2 |
| 0x02 | ins_size_ | 方法参数占用的寄存器数(入参) | 2 |
| 0x04 | outs_size_ | 调用其他方法所需的最大出参寄存器数(临时参数空间) | 2 |
| 0x06 | tries_size_ | try-catch 块数量,非 0 时表示有异常处理结构 | 2 |
| 0x08 | debug_info_off_ | 调试信息在 DEX 文件中的偏移 | 4 |
| 0x0C | insns_size_in_code_units_ | 指令数组长度(单位为 2 字节 code unit) | 4 |
| 共计 | 16 字节 |
CodeItem 前 16 字节是方法的执行元信息,后面的 insns_ 是变长的字节码数组,长度由 insns_size_in_code_units_ 决定,之后可能还有异常处理相关结构(try_items 和 catch_handlers)。
TryItem
TryItem 结构体源码如下 :
// Raw try_item.
struct TryItem {uint32_t start_addr_;uint16_t insn_count_;uint16_t handler_off_;
};
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/libdexfile/dex/dex_file_structs.h;l=196
| 字段名 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| start_addr_ | uint32_t | 指向 code_item->insns[] 的某个偏移,表示 try 块的起始位置(单位为 16-bit 指令) |
| insn_count_ | uint16_t | try 块中包含多少条指令(单位为 16-bit 指令) |
| handler_off_ | uint16_t | 是 hander 结构的偏移,这个偏移是从 insns_ + sizeof(TryItem) * tries_size_ 开始的,用于描述 catch/finally 的处理逻辑 |
完整示例:带各种 TryItem 情况的 Kotlin 类
package com.cyrus.example.shellclass TryItemExample {// ✅ 0. 没有 try-catch(不会生成 TryItem)fun noTryCatch(): Int {val a = 1val b = 2return a + b}// ✅ 1. 简单 try-catch(一个 TryItem)fun simpleTryCatch(): String {return try {val x = 10 / 2"Result: $x"} catch (e: Exception) {"Caught Exception"}}// ✅ 2. 多个 catch 分支(一个 TryItem,多个 handler entry)fun multiCatch(input: String?): Int {return try {input!!.length} catch (e: NullPointerException) {-1} catch (e: Exception) {-2}}// ✅ 3. try-catch-finally(一个 TryItem + finally handler)fun tryCatchFinally(): Int {return try {1 / 0} catch (e: ArithmeticException) {-100} finally {println("finally block executed")}}// ✅ 4. 嵌套 try-catch(两个 TryItem,嵌套结构)fun nestedTryCatch(): String {return try {try {val data = "123".toInt()"Parsed: $data"} catch (e: NumberFormatException) {"Inner Catch"}} catch (e: Exception) {"Outer Catch"}}// ✅ 5. 只有 finally,无 catch(一个 TryItem,无 handler entry)fun onlyFinally(): Int {try {val x = 1 + 1} finally {println("executing finally without catch")}return 0}// ✅ 6. 多个独立 try 块(多个 TryItem,非嵌套)fun multipleTryBlocks(): Int {try {val a = 10 / 2} catch (e: Exception) {println("First catch")}try {val b = "abc".toInt()} catch (e: NumberFormatException) {println("Second catch")}return 0}
}
编译运行得到 dex 文件
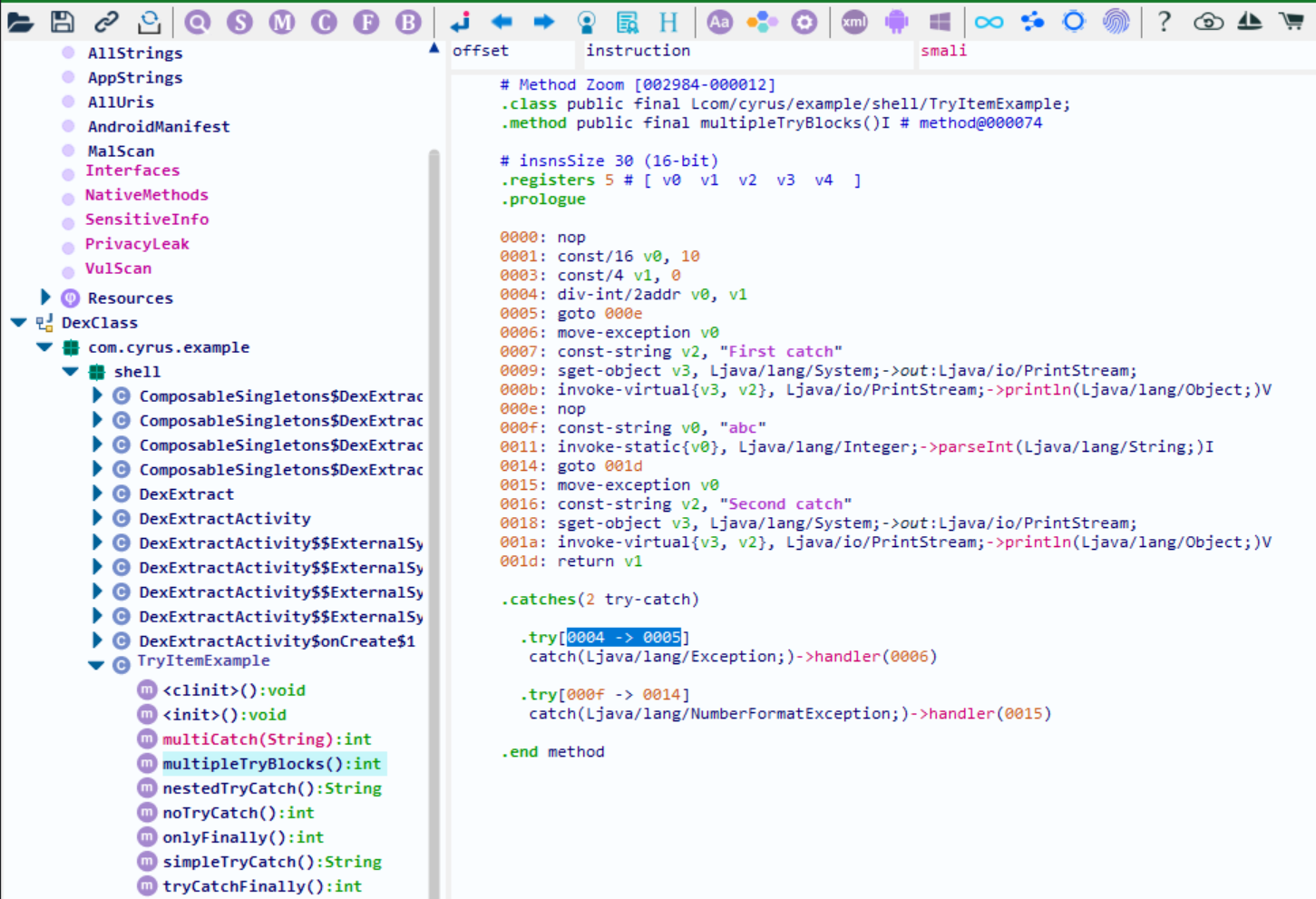
通过 GDA 查看 dex 中 multipleTryBlocks 函数的 TryItem 信息,可以看到 0004 到 0005 就是第一个 try 块的开始和结束地址
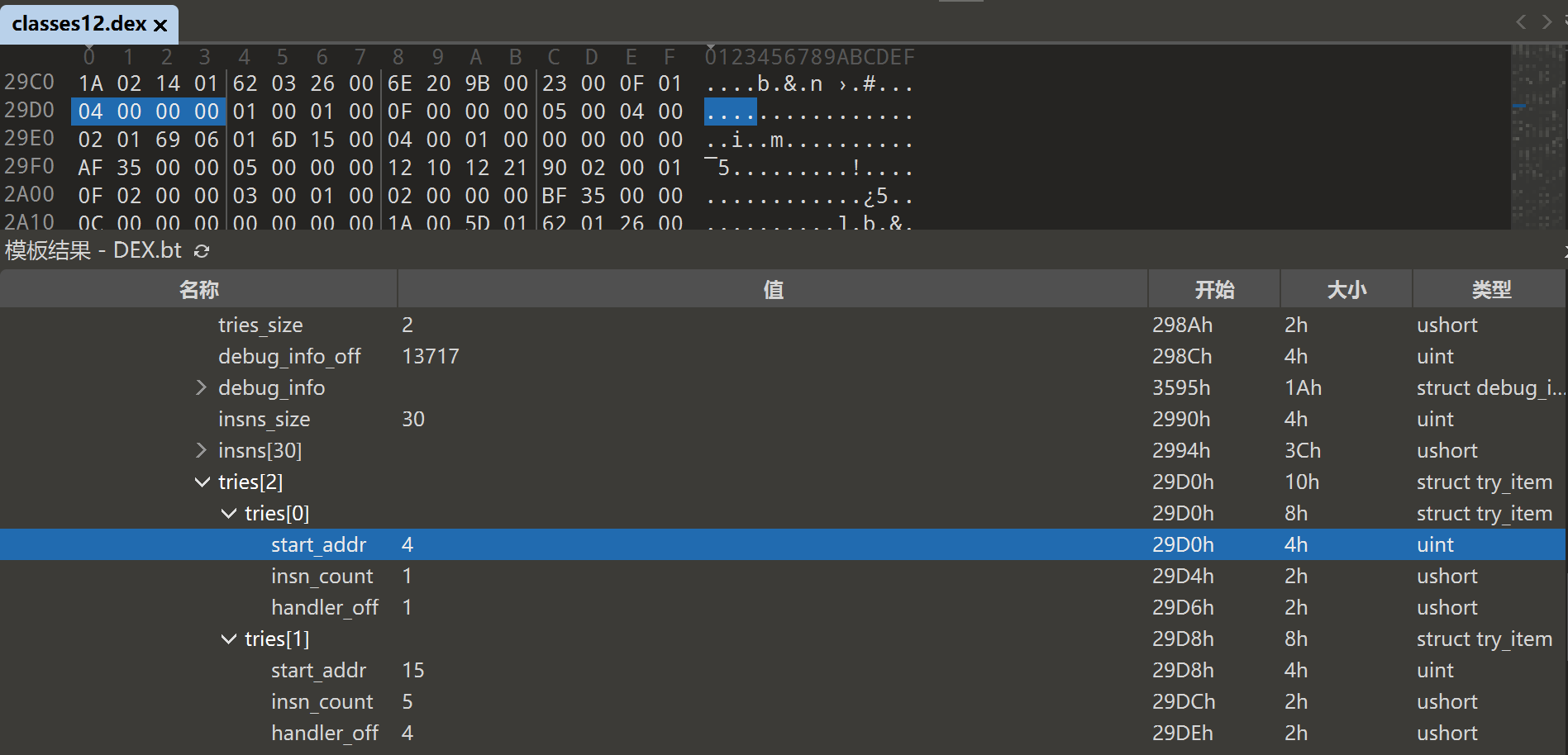
在 010Editor 中打开 dex ,在如下路径
dex_class_defs/class_def[17]/class_def[11] public final com.cyrus.example.shell.TryItemExample/class_data/virtual_methods/method[1] public final int com.cyrus.example.shell.TryItemExample.multipleTryBlocks()/code/tries[2]
可以看到 TryItem 数据
CatchHandlerItem
在 DEX 文件中,TryItem 表示一个异常捕获区域,其对应的异常处理器(handler)由 remaining_count_ 指示 catch/finally 块的数量和类型:
-
如果 remaining_count_ <= 0 表示最后一个是 finally 块。
-
如果 remaining_count_ > 0 表示只有 catch 块。
-
remaining_count_ 的绝对值表示 catch 块的个数。
-
如果 remaining_count_ == 0 表示没有 catch 块,只有 finally 块。
CatchHandlerItem:表示一个 catch 分支(即一个异常类型和对应的处理地址)。
class CatchHandlerIterator {...struct CatchHandlerItem {dex::TypeIndex type_idx_; // 捕获异常的类型索引(指向 Dex 文件中的 type_ids 表)uint32_t address_; // 异常处理器的代码地址(从 code_item.insns 的偏移量)} handler_;const uint8_t* current_data_; // the current handler in dex file.int32_t remaining_count_; // number of handlers not read.bool catch_all_; // is there a handler that will catch all exceptions in case// that all typed handler does not match.
};
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:art/libdexfile/dex/dex_file_exception_helpers.h;l=67
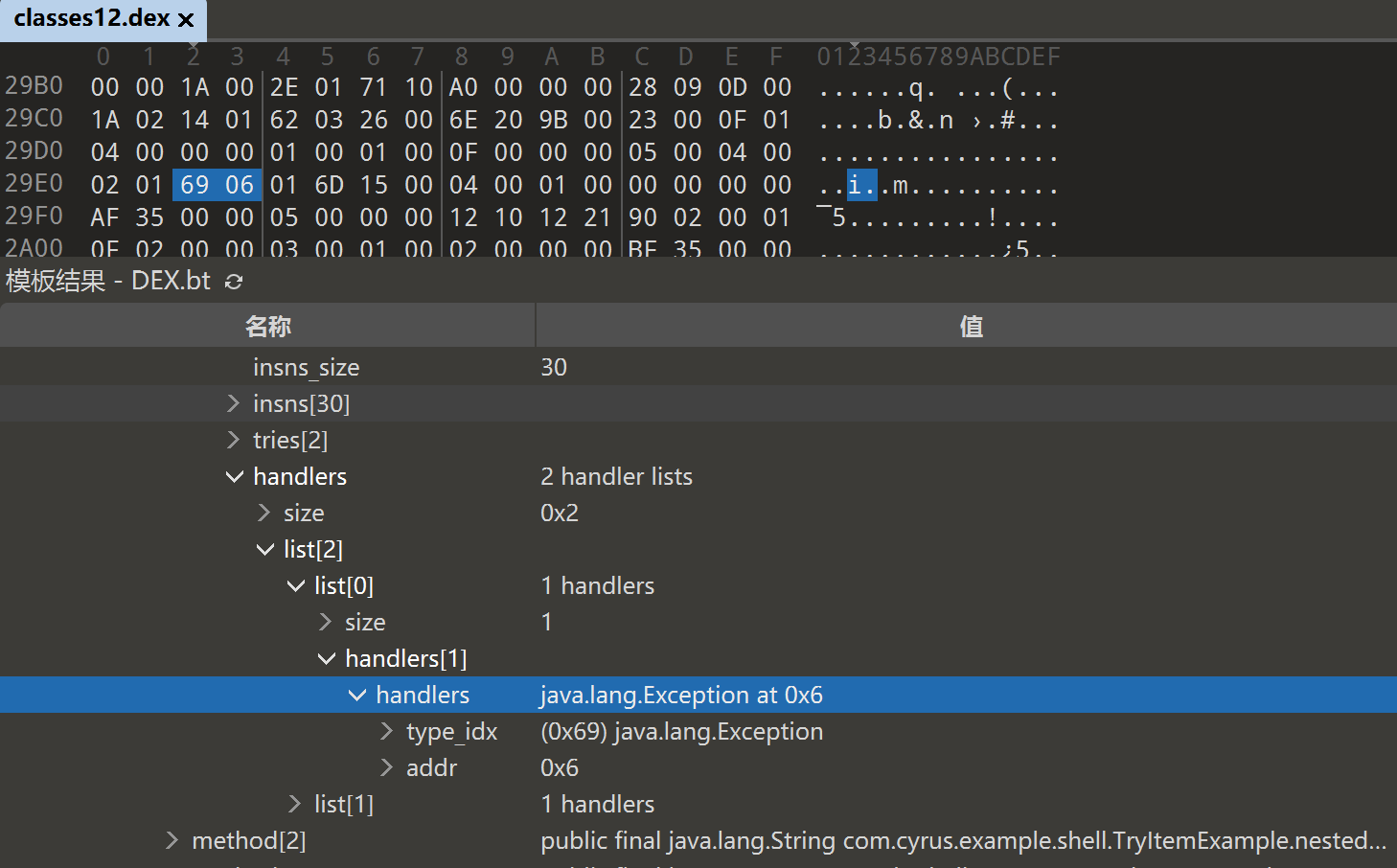
在 010Editor 中打开 dex ,在如下路径
dex_class_defs/class_def[17]/class_def[11] public final com.cyrus.example.shell.TryItemExample/class_data/virtual_methods/method[1] public final int com.cyrus.example.shell.TryItemExample.multipleTryBlocks()/code/handlers
可以看到 CatchHandlerItem 数据
一个 TryItem 对应一个 CatchHandlerIterator ,CatchHandlerIterator 中有一个或多个 CatchHandlerItem,共同组成 try catch/finally 块。
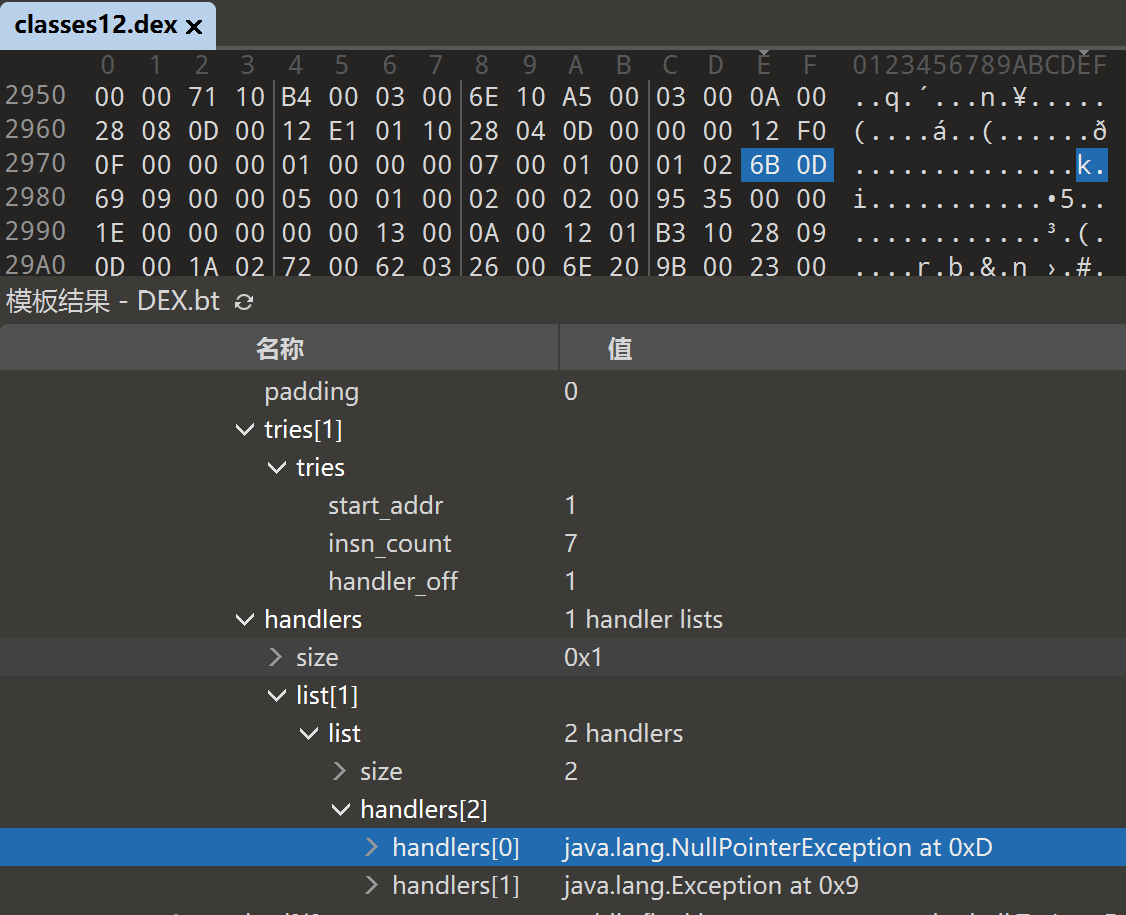
CodeItem 的长度计算和 dump
CodeItem 的长度计算和 dump,两种情况:
-
无异常处理
-
有异常处理
具体实现代码在 FART 项目 art/runtime/art_method.cc 的 dumpArtMethod 函数里
extern "C" void dumpArtMethod(ArtMethod * artmethod) SHARED_LOCKS_REQUIRED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {// 分配临时路径缓冲区char *dexfilepath = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * 2000);if (dexfilepath == nullptr) {LOG(INFO) << "ArtMethod::dumpArtMethod invoked, methodname: "<< PrettyMethod(artmethod).c_str()<< " malloc 2000 byte failed";return;}// 获取进程名(用于保存路径)int fcmdline = -1;char szCmdline[64] = { 0 };char szProcName[256] = { 0 };int procid = getpid();sprintf(szCmdline, "/proc/%d/cmdline", procid);fcmdline = open(szCmdline, O_RDONLY, 0644);if (fcmdline > 0) {read(fcmdline, szProcName, 256);close(fcmdline);}// 如果成功获取进程名if (szProcName[0]) {// 获取方法所属的 DexFileconst DexFile *dex_file = artmethod->GetDexFile();const char *methodname = PrettyMethod(artmethod).c_str();const uint8_t *begin_ = dex_file->Begin(); // dex 数据起始地址size_t size_ = dex_file->Size(); // dex 大小// 创建 fart 路径memset(dexfilepath, 0, 2000);sprintf(dexfilepath, "%s", "/sdcard/fart");mkdir(dexfilepath, 0777);// 创建 fart/进程名 路径memset(dexfilepath, 0, 2000);sprintf(dexfilepath, "/sdcard/fart/%s", szProcName);mkdir(dexfilepath, 0777);// 保存 dex 文件到 /sdcard/fart/进程名/xxx_dexfile.dexmemset(dexfilepath, 0, 2000);sprintf(dexfilepath, "/sdcard/fart/%s/%d_dexfile.dex", szProcName, (int)size_);int dexfilefp = open(dexfilepath, O_RDONLY, 0666);if (dexfilefp > 0) {// 如果文件已存在,不再写入close(dexfilefp);dexfilefp = 0;} else {// 写入完整 dex 数据dexfilefp = open(dexfilepath, O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0666);if (dexfilefp > 0) {write(dexfilefp, (void *) begin_, size_);fsync(dexfilefp);close(dexfilefp);}}// 获取该方法的 CodeItem(即字节码结构体)const DexFile::CodeItem * code_item = artmethod->GetCodeItem();if (LIKELY(code_item != nullptr)) {int code_item_len = 0;uint8_t *item = (uint8_t *) code_item;// 如果有异常处理结构,计算尾部偏移if (code_item->tries_size_ > 0) {const uint8_t *handler_data = (const uint8_t *) (DexFile::GetTryItems(*code_item, code_item->tries_size_));// 解析 handler 数据结构,返回 handler 数据结束的指针位置uint8_t *tail = codeitem_end(&handler_data);code_item_len = (int) (tail - item);} else {// 没有 try 块,长度 = 16字节头部 + 指令长度(每个指令2字节)code_item_len = 16 + code_item->insns_size_in_code_units_ * 2;}// 组合保存路径memset(dexfilepath, 0, 2000);int size_int = (int) dex_file->Size();uint32_t method_idx = artmethod->get_method_idx();sprintf(dexfilepath, "/sdcard/fart/%s/%d_%ld.bin", szProcName, size_int, gettidv1());// 打开保存 CodeItem 信息的文件int fp2 = open(dexfilepath, O_CREAT | O_APPEND | O_RDWR, 0666);if (fp2 > 0) {lseek(fp2, 0, SEEK_END);// 写入方法信息(name、method_idx、offset、code_item_len)memset(dexfilepath, 0, 2000);int offset = (int)(item - begin_);sprintf(dexfilepath,"{name:%s,method_idx:%d,offset:%d,code_item_len:%d,ins:",methodname, method_idx, offset, code_item_len);int contentlength = strlen(dexfilepath);write(fp2, (void *) dexfilepath, contentlength);// base64 编码指令数据并写入long outlen = 0;char *base64result = base64_encode((char *) item, (long)code_item_len, &outlen);write(fp2, base64result, outlen);write(fp2, "};", 2);fsync(fp2);close(fp2);// 清理内存if (base64result != nullptr) {free(base64result);base64result = nullptr;}}}}// 释放路径缓冲区if (dexfilepath != nullptr) {free(dexfilepath);dexfilepath = nullptr;}
}
解析 CodeItem 的异常处理数据部分,返回 handler 数据结束的指针位置
uint8_t *codeitem_end(const uint8_t **pData) {// 读取 handler 列表的数量(即有多少个 try 块)uint32_t num_of_list = DecodeUnsignedLeb128(pData);// 遍历每个 try 块的 handler 列表for (; num_of_list > 0; num_of_list--) {// 读取当前 handler 列表中 handler 的数量,可能为负值,表示存在 catch-all handlerint32_t num_of_handlers = DecodeSignedLeb128(pData);// 取绝对值,得到实际的 type-handler 对数量int num = num_of_handlers;if (num_of_handlers <= 0) {num = -num_of_handlers; // catch-all handler 也算在内,但单独处理}// 读取每个 handler 的 type_idx 和 addressfor (; num > 0; num--) {DecodeUnsignedLeb128(pData); // type_idxDecodeUnsignedLeb128(pData); // address}// 如果存在 catch-all handler,再额外读取一个地址if (num_of_handlers <= 0) {DecodeUnsignedLeb128(pData); // catch-all address}}// 此时 *pData 已指向异常处理部分结束的位置return (uint8_t *)(*pData);
}
如何实现主动调用?
fart 函数中遍历当前 App 的 ClassLoader,拿到 ClassLoader 需要判断不是系统的 BootClassLoader,不然会把系统框架的 dex dump 下来
public static void fart() {ClassLoader appClassloader = getClassloader();if(appClassloader == null){Log.e("ActivityThread", "appClassloader is null");return;}if(appClassloader.toString().indexOf("java.lang.BootClassLoader") == -1){fartWithClassLoader(appClassloader);}ClassLoader tmpClassloader = appClassloader;ClassLoader parentClassloader = appClassloader.getParent();while(parentClassloader != null){if(parentClassloader.toString().indexOf("java.lang.BootClassLoader") == -1){fartWithClassLoader(parentClassloader);}tmpClassloader = parentClassloader;parentClassloader = parentClassloader.getParent();}
}
fartWithClassLoader 函数中遍历 ClassLoader 中的所有 DexFile,获取所有类名,并调用 native 方法 dumpMethodCode。
public static void fartWithClassLoader(ClassLoader appClassloader) {Log.i("ActivityThread", "fartWithClassLoader " + appClassloader.toString());// 用于存放获取到的 dexFile 对象List<Object> dexFilesArray = new ArrayList<Object>();// 获取 DexPathList 对象实例Object pathList_object = getFieldOjbect("dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader", appClassloader, "pathList");// 获取 dexElements 字段,类型为 DexPathList$Element[],每个 element 封装了 dexFileObject[] ElementsArray = (Object[]) getFieldOjbect("dalvik.system.DexPathList", pathList_object, "dexElements");// 声明 dexElements 中的 dexFile 字段Field dexFile_fileField = null;try {dexFile_fileField = (Field) getClassField(appClassloader, "dalvik.system.DexPathList$Element", "dexFile");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 通过类加载器反射获取 dalvik.system.DexFile 类Class DexFileClazz = null;try {DexFileClazz = appClassloader.loadClass("dalvik.system.DexFile");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 要调用的 native 方法Method getClassNameList_method = null;Method defineClass_method = null;Method dumpMethodCode_method = null;// 遍历 DexFile 类中的方法,设置需要的 native 方法强制可访问for (Method field : DexFileClazz.getDeclaredMethods()) {if (field.getName().equals("getClassNameList")) {getClassNameList_method = field;getClassNameList_method.setAccessible(true);}if (field.getName().equals("defineClassNative")) {defineClass_method = field;defineClass_method.setAccessible(true);}if (field.getName().equals("dumpMethodCode")) {dumpMethodCode_method = field;dumpMethodCode_method.setAccessible(true);}}// 获取 mCookie 字段(DexFile 中指向 native Dex 的句柄)Field mCookiefield = getClassField(appClassloader, "dalvik.system.DexFile", "mCookie");// 遍历每一个 dex element(即每个 dex 文件)for (int j = 0; j < ElementsArray.length; j++) {Object element = ElementsArray[j];Object dexfile = null;try {// 通过反射获取 DexFile 对象dexfile = (Object) dexFile_fileField.get(element);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (dexfile == null) {continue;}// 加入列表dexFilesArray.add(dexfile);// 获取 native mCookie 对象Object mcookie = getClassFieldObject(appClassloader, "dalvik.system.DexFile", dexfile, "mCookie");if (mcookie == null) {continue;}// 调用 native 方法 getClassNameList(mcookie) 获取 dex 中包含的类名数组String[] classnames = null;try {classnames = (String[]) getClassNameList_method.invoke(dexfile, mcookie);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();continue;} catch (Error e) {e.printStackTrace();continue;}// 遍历所有类名,对每个类调用 dumpMethodCodeif (classnames != null) {for (String eachclassname : classnames) {loadClassAndInvoke(appClassloader, eachclassname, dumpMethodCode_method);}}}return;
}
主动加载 dex 中的所有类需要对 dex 文件解析,获取 dex 中的所有类列表,两种解决方案:
-
手动解析 dex 文件
-
直接调用 aosp 源码中已有的 api:getClassNameList 即可(需要通过反射一步步获取当前 ClassLoader 当中的 mCookie)
拿到 ClassLoader 的 dexElements ,迭代 dexElements 通过反射拿到 DexFile 的 mCookie

https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/DexPathList.java;l=69
调用 DexFile.getClassNameList 传递 mCookie 得到 dex 的 class list

https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android10-release:libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/DexFile.java;l=432
拿到 ClassNameList 后,调用 loadClassAndInvoke 进行主动加载;
LoadClassAndInvoke 中对类进行加载,遍历类中构造函数和普通函数,进行主动调用。
public static void loadClassAndInvoke(ClassLoader appClassloader, String eachclassname, Method dumpMethodCode_method) {Log.i("ActivityThread", "go into loadClassAndInvoke->" + "classname:" + eachclassname);Class resultclass = null;try {// 使用给定的 ClassLoader 加载指定类名的类resultclass = appClassloader.loadClass(eachclassname);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return;} catch (Error e) {e.printStackTrace();return;}// 如果类加载成功if (resultclass != null) {try {// 获取该类的所有构造方法(包括 private 的)Constructor<?> cons[] = resultclass.getDeclaredConstructors();for (Constructor<?> constructor : cons) {if (dumpMethodCode_method != null) {try {// 调用 native 方法 dumpMethodCode 传入构造方法对象// 发起主动调用 并 dump methoddumpMethodCode_method.invoke(null, constructor);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();continue;} catch (Error e) {e.printStackTrace();continue;}} else {Log.e("ActivityThread", "dumpMethodCode_method is null ");}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (Error e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {// 获取该类的所有方法(包括 private 的)Method[] methods = resultclass.getDeclaredMethods();if (methods != null) {for (Method m : methods) {if (dumpMethodCode_method != null) {try {// 调用 native 方法 dumpMethodCodedumpMethodCode_method.invoke(null, m);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();continue;} catch (Error e) {e.printStackTrace();continue;}} else {Log.e("ActivityThread", "dumpMethodCode_method is null ");}}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (Error e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
通过 loadClass 加载类,为什么不用 Class.forName?因为 Class.forName 会调用类的初始化方法,有一些对抗手段会在类初始化中执行,所以用 loadClass,loadClass 不会调用类的初始化方法。
resultclass = appClassloader.loadClass(eachclassname);
进入到 ArtMethod 的 Invoke 方法后,识别出是我们自己发起的主动调用后,执行 dumpArtMethod
void ArtMethod::Invoke(Thread* self, uint32_t* args,uint32_t args_size, JValue* result,const char* shorty) {// 若 self 为空,直接 dump 当前 ArtMethodif (self == nullptr) {dumpArtMethod(this);return;}...
}


)




