- 1. QML中容器控件全解:构建灵活界面的基石
- 1.1. Item(万物容器)
- 1.2. Rectangle(视觉容器)
- 1.3. ListView(动态列表容器)
- 1.4. Frame(表单容器)
- 1.5. SwipeView(页面容器)
- 1.6. TabBar(导航容器)
- 1.7. SwipeView 和 TabBar 的区别
- 1.7.1. 功能和交互方式
- 1.7.2. 交互方式
- 1.7.3. 视觉表现
- 1.7.4. 适用场景
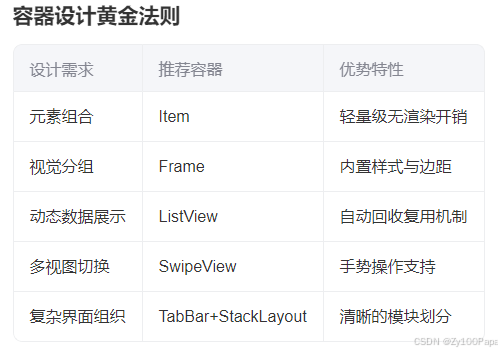
- 2. 容器设计黄金法则
1. QML中容器控件全解:构建灵活界面的基石
在智能设备井喷的时代,QML容器控件如同"数字乐高",通过巧妙的组合艺术,将简单元素转化为功能强大的交互界面。
本篇将揭秘工业HMI、车载中控等专业场景中最核心的容器控件,带您掌握界面架构设计的精髓。
1.1. Item(万物容器)
设计哲学:
作为QML世界的"原子单位",Item是其他所有控件的基类,承担着界面元素组织者的角色。
Item {id: sensorGroupwidth: 300; height: 200// 组合多个传感器显示模块TemperatureDisplay { anchors.left: parent.left }PressureIndicator { anchors.right: parent.right }StatusLed {anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenteranchors.bottom: parent.bottom}// 统一控制可见性visible: systemStatus === "normal"
}实战技巧:
通过visible属性实现整体显隐控制
使用anchors进行相对定位
作为自定义组件的基容器
1.2. Rectangle(视觉容器)
工业场景:
在设备状态看板中,用于创建带背景色的信息区块,提升界面层次感。
Rectangle {radius: 8border.color: "#2196F3"color: "#E3F2FD"Column {spacing: 10anchors.fill: parentpadding: 15Text { text: "电机状态监控"; font.bold: true }ProgressBar { value: motorStatus.speed }Row {spacing: 5CheckBox { text: "过热保护" }CheckBox { text: "震动报警" }}}
}设计规范:
使用radius实现圆角现代化设计
通过嵌套布局构建复合组件
用颜色区分不同功能区域
1.3. ListView(动态列表容器)
车载系统应用:
用于音乐列表、导航历史等需要动态加载的滚动列表。
ListView {width: 240height: 300model: musicListModelspacing: 2clip: truedelegate: Rectangle {width: ListView.view.widthheight: 40color: index%2 ? "#FAFAFA" : "white"Text {text: model.titleanchors.verticalCenter: parent.verticalCentercolor: model.isPlaying ? "#2196F3" : "black"}MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: musicPlayer.selectTrack(model.id)}}ScrollBar.vertical: ScrollBar { policy: ScrollBar.AlwaysOn }
}性能优化:
使用clip:true防止渲染溢出
通过delegate复用机制提升性能
集成自定义滚动条
1.4. Frame(表单容器)
医疗设备应用:
用于参数设置面板等需要明确视觉边界的表单组合。
Frame {background: Rectangle {color: "#FFF3E0"border.color: "#FFA726"radius: 4}ColumnLayout {spacing: 12TextField {placeholderText: "患者ID"Layout.fillWidth: true}Slider {id: pressureSliderfrom: 0to: 100Layout.fillWidth: true}Button {text: "保存预设"Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignRight}}
}交互设计:
自定义边框颜色增强辨识度
内置padding保持内容间距
配合Layout控件实现自适应
1.5. SwipeView(页面容器)
工业平板应用:
实现多页面滑动切换,适用于设备监控的多视图场景。
SwipeView {id: viewanchors.fill: parentcurrentIndex: 0// 页面1:实时监控RealTimeMonitor { }// 页面2:历史数据HistoryChart { }// 页面3:报警记录AlarmList { }
}PageIndicator {count: view.countcurrentIndex: view.currentIndexanchors.bottom: view.bottom
}进阶用法:
结合PageIndicator显示进度
通过currentIndex控制页面跳转
支持手势滑动操作
1.6. TabBar(导航容器)
智能家居中控应用:
实现多标签页导航,管理不同功能模块。
Column {anchors.fill: parentTabBar {id: barwidth: parent.widthTabButton { text: "环境监测" }TabButton { text: "设备控制" }TabButton { text: "能耗统计" }}StackLayout {width: parent.widthheight: parent.height - bar.heightcurrentIndex: bar.currentIndexEnvironmentPanel { }DeviceController { }EnergyDashboard { }}
}1.7. SwipeView 和 TabBar 的区别
1.7.1. 功能和交互方式
-
SwipeView:
SwipeView 是一个基于滑动的导航控件,用户可以通过水平滑动手势在不同页面之间切换。它适合需要通过滑动手势快速切换页面的场景,比如轮播图、选项卡、向导等。 -
TabBar:
TabBar 是一个标签栏控件,用户通过点击标签按钮切换页面。它适合需要通过标签明确指示当前页面的场景,比如多页面应用的导航栏。
1.7.2. 交互方式
-
SwipeView:
主要通过滑动手势进行页面切换,支持触摸屏设备的自然交互。 -
TabBar:
主要通过点击标签按钮进行页面切换,适合需要明确的页面导航和选择的场景。
1.7.3. 视觉表现
-
SwipeView:
SwipeView 本身是不可见的,通常需要与页面指示器(如 PageIndicator)结合使用,以显示当前页面的位置。 -
TabBar:
TabBar 是一个可视化的标签栏,通常显示在页面顶部或底部,提供明确的导航指示。
1.7.4. 适用场景
-
SwipeView:
适合需要滑动切换页面的场景,比如设置页面、欢迎引导页面等。 -
TabBar:
适合需要通过标签导航的场景,比如多页面应用的底部导航栏。
2. 容器设计黄金法则
掌握这些容器控件,您将能像搭积木一样构建出专业级工业界面。立即用这些代码片段开启您的下一个项目吧!




