DEA-Net: Single image dehazing based on detail-enhanced convolution and content-guided attention
论文地址:
论文解决的问题:
如何解决的:
应用场景:
适用于哪种目标检测:
即插即用代码:
该模块可以缝合的位置:
论文地址:
[2301.04805] DEA-Net: Single image dehazing based on detail-enhanced convolution and content-guided attention![]() https://ar5iv.labs.arxiv.org/html/2301.04805?_immersive_translate_auto_translate=1
https://ar5iv.labs.arxiv.org/html/2301.04805?_immersive_translate_auto_translate=1
论文解决的问题:
- 单幅图像去雾:在有雾条件下拍摄的图像通常会出现对比度低、颜色失真和细节模糊的问题,这给图像分析和理解带来了挑战。
如何解决的:
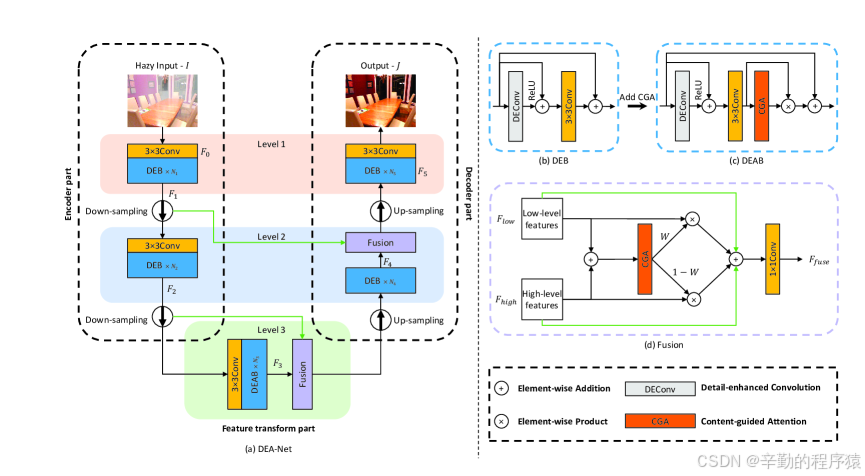
- 细节增强卷积(DEConv):
- 差异卷积:通过计算输入特征图与其经过不同卷积核处理后的特征图之间的差异,来捕获更精细的细节。
- 参数化技术:通过重新参数化减少模型的参数数量和计算量,使得模型更加高效。
- 内容引导注意力(CGA):
- 空间重要性图(SIM):为每个特征通道生成一个空间重要性图,强调图像中的重要区域。
- 注意力机制:基于SIM,模型能够自适应地调整每个特征通道的权重,从而更好地关注关键信息。
- 混合融合方案:
- 特征融合:将低层特征(包含丰富的细节信息)与高层特征(包含语义信息)相结合,通过CGA指导的融合策略,生成更高质量的输出图像。
应用场景:
- 户外监控:在有雾的天气条件下,提高监控视频的清晰度,帮助监控人员更好地识别目标。
- 自动驾驶:在恶劣天气下,去雾技术可以提高自动驾驶系统的感知能力,确保行车安全。
- 遥感图像处理:提高遥感图像的清晰度,有助于更准确地监测和分析地理信息。
适用于哪种目标检测:
- 低能见度条件下的目标检测:在有雾或雾霾等低能见度条件下,传统的目标检测算法性能会显著下降。DEA-Net通过去雾处理,可以显著提高这些条件下的图像质量,从而改善目标检测算法的性能。
- 小目标和密集目标检测:去雾后的图像能够更好地保留小目标的细节和区分密集目标,这对于小目标检测和密集目标检测(如人群计数)尤为重要。
- 夜间或光照不足条件下的目标检测:虽然DEA-Net主要针对去雾,但其增强图像细节的能力也可能有助于改善夜间或光照不足条件下的目标检测。
DEA-Net通过其创新的细节增强和内容引导注意力机制,不仅能够有效去雾,还能为各种目标检测任务提供更高质量的输入图像,从而提高目标检测的准确性和可靠性。
即插即用代码:
import math
import torch
from torch import nn
from einops.layers.torch import Rearrange
class Conv2d_cd(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=False, theta=1.0):super(Conv2d_cd, self).__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding,dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=bias)self.theta = thetadef get_weight(self):conv_weight = self.conv.weightconv_shape = conv_weight.shapeconv_weight = Rearrange('c_in c_out k1 k2 -> c_in c_out (k1 k2)')(conv_weight)conv_weight_cd = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(conv_shape[0], conv_shape[1], 3 * 3).fill_(0)conv_weight_cd[:, :, :] = conv_weight[:, :, :]conv_weight_cd[:, :, 4] = conv_weight[:, :, 4] - conv_weight[:, :, :].sum(2)conv_weight_cd = Rearrange('c_in c_out (k1 k2) -> c_in c_out k1 k2', k1=conv_shape[2], k2=conv_shape[3])(conv_weight_cd)return conv_weight_cd, self.conv.biasclass Conv2d_ad(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=False, theta=1.0):super(Conv2d_ad, self).__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding,dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=bias)self.theta = thetadef get_weight(self):conv_weight = self.conv.weightconv_shape = conv_weight.shapeconv_weight = Rearrange('c_in c_out k1 k2 -> c_in c_out (k1 k2)')(conv_weight)conv_weight_ad = conv_weight - self.theta * conv_weight[:, :, [3, 0, 1, 6, 4, 2, 7, 8, 5]]conv_weight_ad = Rearrange('c_in c_out (k1 k2) -> c_in c_out k1 k2', k1=conv_shape[2], k2=conv_shape[3])(conv_weight_ad)return conv_weight_ad, self.conv.biasclass Conv2d_rd(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=2, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=False, theta=1.0):super(Conv2d_rd, self).__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding,dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=bias)self.theta = thetadef forward(self, x):if math.fabs(self.theta - 0.0) < 1e-8:out_normal = self.conv(x)return out_normalelse:conv_weight = self.conv.weightconv_shape = conv_weight.shapeif conv_weight.is_cuda:conv_weight_rd = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(conv_shape[0], conv_shape[1], 5 * 5).fill_(0)else:conv_weight_rd = torch.zeros(conv_shape[0], conv_shape[1], 5 * 5)conv_weight = Rearrange('c_in c_out k1 k2 -> c_in c_out (k1 k2)')(conv_weight)conv_weight_rd[:, :, [0, 2, 4, 10, 14, 20, 22, 24]] = conv_weight[:, :, 1:]conv_weight_rd[:, :, [6, 7, 8, 11, 13, 16, 17, 18]] = -conv_weight[:, :, 1:] * self.thetaconv_weight_rd[:, :, 12] = conv_weight[:, :, 0] * (1 - self.theta)conv_weight_rd = conv_weight_rd.view(conv_shape[0], conv_shape[1], 5, 5)out_diff = nn.functional.conv2d(input=x, weight=conv_weight_rd, bias=self.conv.bias,stride=self.conv.stride, padding=self.conv.padding, groups=self.conv.groups)return out_diffclass Conv2d_hd(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=False, theta=1.0):super(Conv2d_hd, self).__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding,dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=bias)def get_weight(self):conv_weight = self.conv.weightconv_shape = conv_weight.shapeconv_weight_hd = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(conv_shape[0], conv_shape[1], 3 * 3).fill_(0)conv_weight_hd[:, :, [0, 3, 6]] = conv_weight[:, :, :]conv_weight_hd[:, :, [2, 5, 8]] = -conv_weight[:, :, :]conv_weight_hd = Rearrange('c_in c_out (k1 k2) -> c_in c_out k1 k2', k1=conv_shape[2], k2=conv_shape[2])(conv_weight_hd)return conv_weight_hd, self.conv.biasclass Conv2d_vd(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=False):super(Conv2d_vd, self).__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding,dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=bias)def get_weight(self):conv_weight = self.conv.weightconv_shape = conv_weight.shapeconv_weight_vd = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(conv_shape[0], conv_shape[1], 3 * 3).fill_(0)conv_weight_vd[:, :, [0, 1, 2]] = conv_weight[:, :, :]conv_weight_vd[:, :, [6, 7, 8]] = -conv_weight[:, :, :]conv_weight_vd = Rearrange('c_in c_out (k1 k2) -> c_in c_out k1 k2', k1=conv_shape[2], k2=conv_shape[2])(conv_weight_vd)return conv_weight_vd, self.conv.biasclass DEConv(nn.Module):def __init__(self, dim):super(DEConv, self).__init__()self.conv1_1 = Conv2d_cd(dim, dim, 3, bias=True)self.conv1_2 = Conv2d_hd(dim, dim, 3, bias=True)self.conv1_3 = Conv2d_vd(dim, dim, 3, bias=True)self.conv1_4 = Conv2d_ad(dim, dim, 3, bias=True)self.conv1_5 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1, bias=True)def forward(self, x):w1, b1 = self.conv1_1.get_weight()w2, b2 = self.conv1_2.get_weight()w3, b3 = self.conv1_3.get_weight()w4, b4 = self.conv1_4.get_weight()w5, b5 = self.conv1_5.weight, self.conv1_5.biasw = w1 + w2 + w3 + w4 + w5b = b1 + b2 + b3 + b4 + b5res = nn.functional.conv2d(input=x, weight=w, bias=b, stride=1, padding=1, groups=1)return resif __name__ == '__main__':block = DEConv(dim=32).cuda()# 输入 B C H Winput = torch.rand(1, 32, 32, 32).cuda()output = block(input)print("输入尺寸:", input.size())print("输出尺寸:", output.size())该模块可以缝合的位置:
- 特征提取层之间:在卷积神经网络(CNN)的特征提取阶段,将DEA-Net作为一个中间层,用于处理由前一卷积层输出的特征图。
- 特征融合层:如果你的网络使用了多尺度或多层次的特征融合,可以在融合之前对每个尺度的特征使用DEA-Net进行去雾处理。
- 辅助网络:如果你使用的是像YOLO或Faster R-CNN这样的目标检测网络,可以将DEA-Net作为一个辅助网络,其输出与主网络的输出合并。
如果你对YOLO感兴趣可以进入交流群:






