1. 背景
在应用的开发过程中,由于初期数据量小,开发人员在写SQL语句时更重视功能上的实现,但当应用系统正式上线后,随着生产数据量的急剧增长,很多SQL 语句开始逐渐暴露出性能问题,对生产的影响也越来越大,此时这些有问题的SQL就成为了整个系统性能的瓶颈,这时必须对它们进行优化。
进行SQL优化,索引将是数据库用来提高性能的最常用工具。所有MySQL列类型可以被索引,对相关列使用索引是提高SELECT操作性能的最佳途径。
2. Bad Case
2.1 count(*)
虽然下面的执行计划命中了 idx_vflag 普通索引,但遍历该二级索引树时,扫描的行数依然很多,接近全表扫描,效率非常低。
MySQL [bussinessc]> show index from bussinessc.t_bussiness;
+------------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+------------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| t_bussiness | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 1779703 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t_bussiness | 0 | uk_bussiness_id | 1 | bussiness_id | A | 1799108 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t_bussiness | 1 | idx_tel | 1 | tel | A | 330417 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t_bussiness | 1 | idx_add_time | 1 | add_time | A | 291181 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t_bussiness | 1 | idx_create_time | 1 | create_time | A | 1190831 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t_bussiness | 1 | idx_update_time | 1 | update_time | A | 1061260 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t_bussiness | 1 | idx_vflag | 1 | vflag | A | 1 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t_bussiness | 1 | idx_tag | 1 | tag | A | 2 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+------------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
8 rows in set (0.002 sec)MySQL [bussinessc]> explain SELECT count(*) FROM bussinessc.t_bussiness \G;*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: t_bussiness partitions: NULLtype: index
possible_keys: NULLkey: idx_vflag key_len: 1ref: NULL rows: 1879793filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using index
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.002 sec)因为 InnoDB 引擎实现了多版本并发控制(MVCC),对同一个表,不同事物在同一时刻,看到的数据可能是不一样的。
所以在 InnoDB 引擎中,不能像在 MyISAM 中直接把对应值存到内存和磁盘文件中,当执行 count(*) 的时候,它需要一行一行的进行统计和计数,并将最终的统计结果返回。
count(*)的改进
在 5.7.18 版本之前,InnoDB 处理 select count(*) 是通过扫描聚簇索引,来获取总记录数。从 5.7.18 版本开始,InnoDB 扫描一个最小的可用的二级索引来获取总记录数,或者由 SQL hint 来告诉优化器使用哪个索引。如果二级索引不存在,InnoDB 将会扫描聚簇索引。
原因:InnoDB是索引组织表,主键索引的叶子节点是数据,而普通索引的叶子节点是主键值,所以普通索引树比主键索引树小很多。对于COUNT(*) 来说,遍历哪颗树都一样,所以mysql优化器会选择最小的树进行遍历。在保证逻辑正确的前提下,尽量减少扫描的数据量。加载同样的数据量, 由于二级索引叶子节点存放的是主键Id,所有走二级索引需要的 io 次数更少。
3. 定位索引
3.1 索引是什么?
索引是对数据库表中一列或多列的值进行排序的一种结构,包含着对数据表里所有记录的引用指针,大多单独存储在磁盘上。使用索引可以提高数据库中特定数据的查询速度,如果表中查询的列有一个索引,Mysql能快速到达一个位置去搜索数据文件,而不必查看所有数据,避免进行全表扫描。
常见索引的数据结构实现,一般可以分为B+tree索引、B-tree索引、Hash索引、Full-text索引和空间索引。
3.2 索引在哪里?
索引是在存储引擎层中实现的,不是在服务器层,所以每种存储引擎的索引都不一定完全相同,也不是所有存储引擎都支持所有的索引类型。
根据存储引擎,可以定义每个表的最大索引和最大索引长度,每种存储引擎对每个表至少支持16个索引,总索引长度至少为256字节。大多数存储引擎有更高的限制。
3.2.1 认识 MySQL 体系
MySQL体系结构,大致分下面几个部分,
客户端连接部分 → MySQL Server部分 → Service & Utilities部分 → SQL处理所需要的模块 → MySQL所支持的各个存储引擎 → 物理存储层
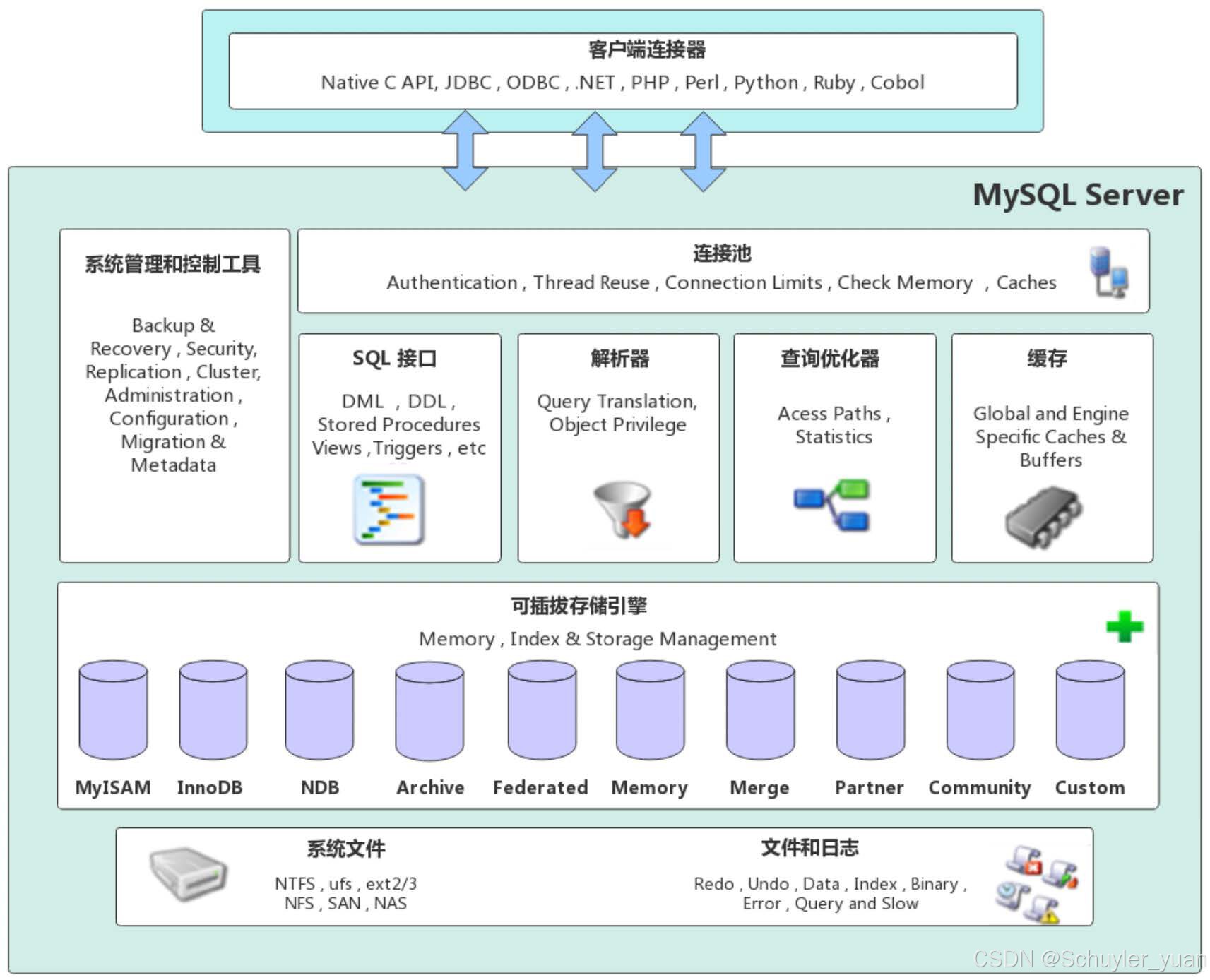
1. 客户端连接部分
- 处理客户端的连接请求,MySQL支持所有的连接类型
2. MySQL Server部分
- 数据库给客户端创建的连接都在connection pool中处理和存储,用一个线程管理一个连接,包括用户认证、安全管理等。
3. Service & Utilities部分
- 管理工具 & 工具集,用于备份恢复、安全管理、集群管理服务&工具
4. SQL处理所需要的模块
- 查询优化,会根据解析树生成执行计划,选择合适的索引,之后会按照执行计划去执行SQL,和各个引擎交互。
- SQL接口(接收用户的SQL命令并处理)
- SQL解析器(负责将请求的SQL解析生成一个"解析树",然后根据一些MySQL规则进一步检查解析树是否合法)
- 查询优化器(对查询语句进行优化,选择合适索引,优化器的作用就是以它认为的最优的执行方案去执行(有时候可能也不是最优),比如多个索 引的时候该如何选择索引,多表查询的时候如何选择关联顺序等。可以说,经过了优化器之后可以说这个语句具体该如何执行就已经定下来)
- 缓存(包括各个引擎的缓存部分,比如InnoDB存储有pool,MyISAM有KeyBuffer等,也会缓存一些权限,是一些session级别的缓存)
5. MySQL所支持的各个存储引擎
- 插件式存储引擎(只要写好跟MySQL Server的接口,任何引擎都可以接入到MySQL里。这也是MySQL流行的原因之一)
6. 物理存储层
- 文件的物理存储,包括二进制日志、数据文件、错误日志、慢查询日志、全日志、redo日志、undo日志等等。
3.2.2 一条Select的执行轨迹
权限校验(如果命中缓存)→ 查询缓存 → 分析器 → 优化器 → 权限校验 → 执行器 → 引擎
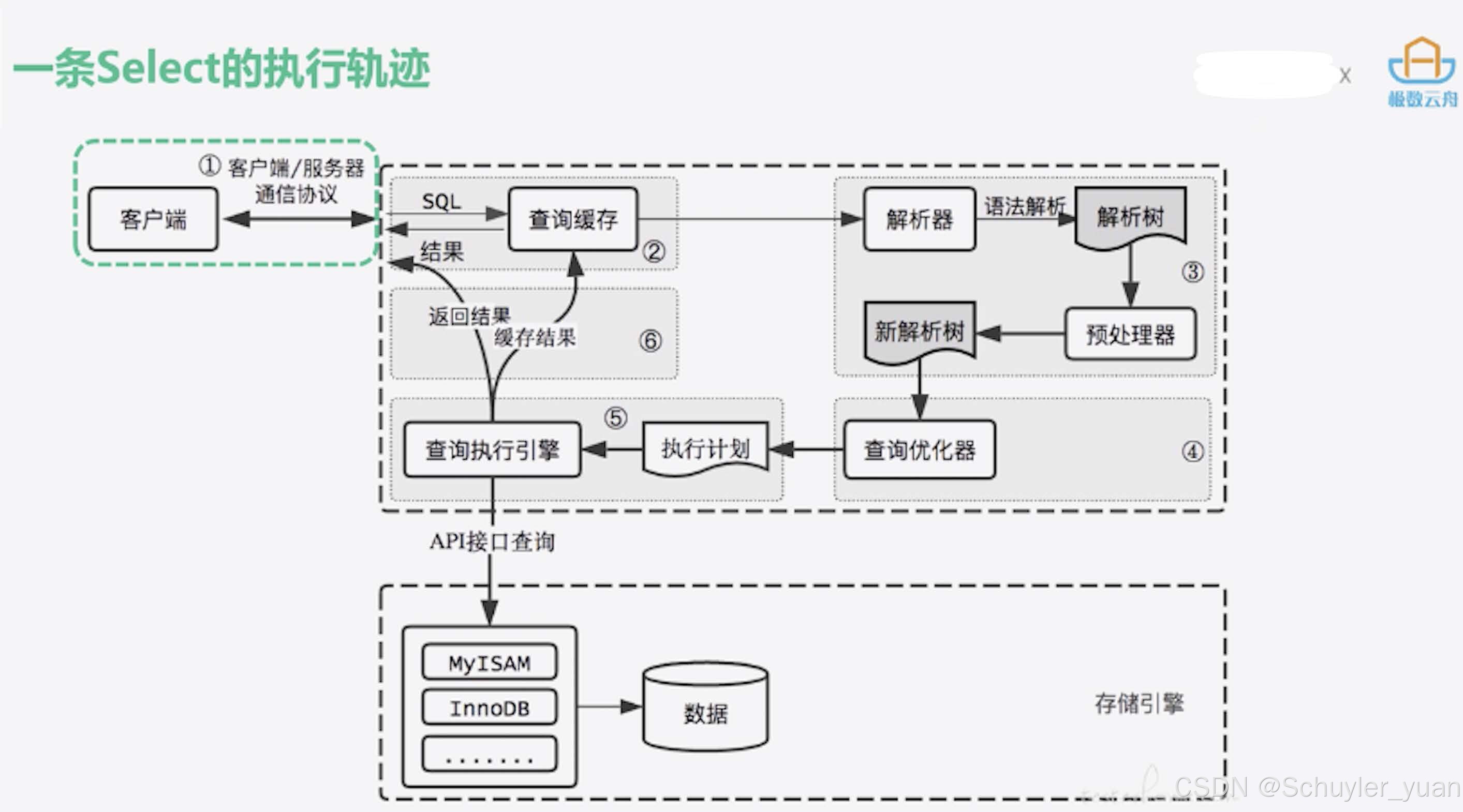
- 客户端通过CS通信协议和MySQL建立连接,
- 查询缓存,这是一个优化查询的地方,如果开启了Query_cache,且在缓存中有完全相同的SQL,则会直接返回结果给客户端,如果没有完全一样的 sql,就会经过解析器进行语法解析,生成解析树,
- 预处理器生成新解析树,
- 查询优化器,生成执行计划,
- 查询引擎执行真正的SQL,此时会根据SQL中的表的存储引擎类型、对应的API接口,与底层存储引擎、缓存或者物理文件进行交互,得到查询结果,由MySQL Server过滤后,缓存起来,返回给客户端。若开启了Query_cache,会将结果完全缓存起来,以后便于直接返回结果,当然这里的sql语句是hash过的。
3.2.3 什么是存储引擎
插件式存储引擎,是 MySQL 中具体与文件打交道的子系统,根据 MySQL AB 公司提供的文件访问层抽象接口定制的一种文件访问机制。作为 MySQL 最重要的特定之一,用户可以根据应用的需要选择存储和索引数据的方式、是否使用事务等,可以理解为表类型。
MySQL 默认支持多种存储引擎,适用于不同领域的数据库应用需要,用户可以选择不同的存储引擎提高应用的效率,提供灵活的存储,甚至还可以定制自己的存储引擎。
MySQL 5.6 之前,默认存储引擎是 MyISAM;5.6 之后,改成了 InnoDB。
3.2.4 常见存储引擎的功能特性
MyISAM 不支持事务,不支持外键,优势在于访问速度快,对事务完整性没有要求,表级锁。
InnoDB 提供了具有提交、回滚和崩溃回复能力的事务安全,相比于 MyISAM,InnoDB 写的处理效率差一些,还会占用更多的磁盘空间来保留数据和索引,表级锁 / 行级锁。
Memory 使用存在于内存中的内容创建表,访问表非常快,由于内存特性,表中的数据容易丢失。
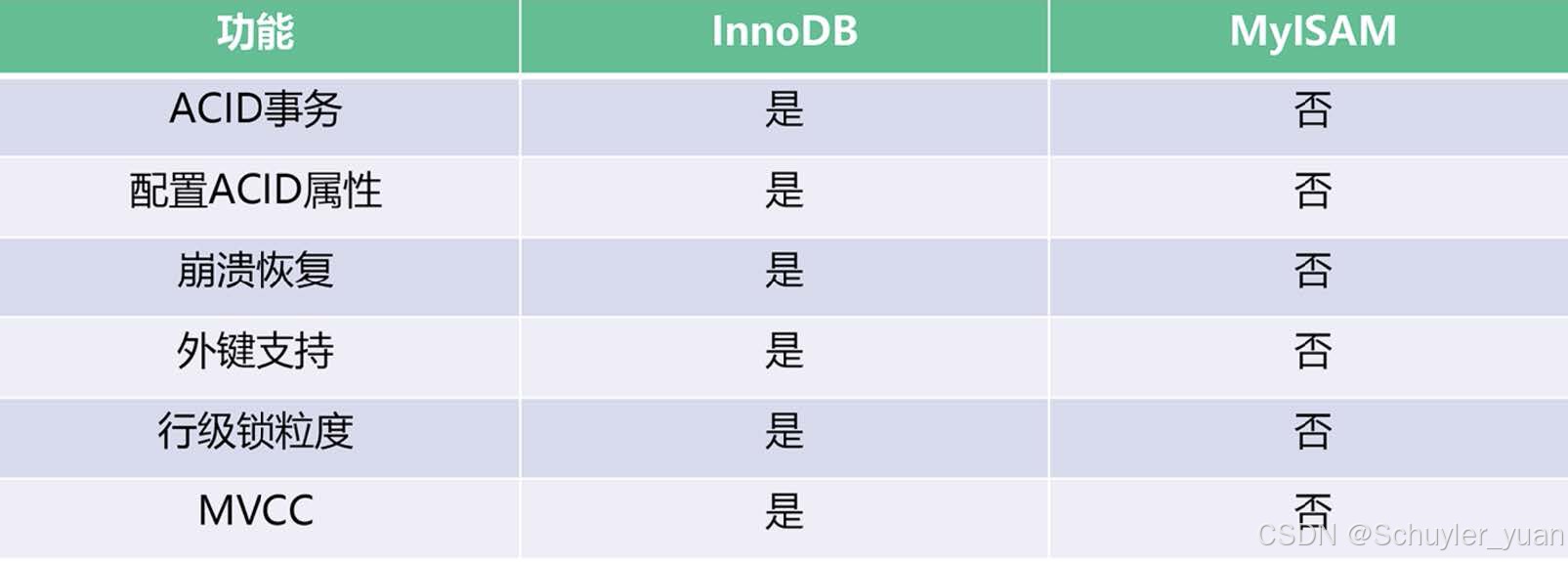
3.2.5 常见存储引擎的存储特性
MyISAM在磁盘上存储成3个文件,文件名和表名相同,扩展名分别是,
- frm(存储表定义)
- MYD(存储数据)
- MYI(存储索引)
InnoDB存储表和索引有两种方式,
- 共享表空间存储(这种方式创建的表的表结构存储在frm文件,数据和索引分别存在不同定义的表空间下,可以是多个文件)
- 多表空间存储(这种方式创建的表的表结构仍然保存在frm文件中,但每个表的数据和索引单独保存在ibd中)
- 即使在多表空间的存储方式下,共享表空间仍然是必须的,InnoDB把内部数据词典和在线重做日志放在这个文件中。
Memory则是使用存在于内存中的内容创建表。每个Memory表只实际对应一个 frm 格式的磁盘文件,一旦服务关闭,表中的数据就会丢失。
3.2.6 常见存储引擎支持的索引数据结构
BTREE索引(B+TREE索引)
- MyISAM、InnoDB的表默认创建的都是BTREE索引,B+Tree是B-tree的升级结构。
Hash索引
- MyISAM 不支持 Hash 索引;InnoDB 支持自适应 Hash 索引,但 InnoDB 中 Hash 索引的创建由存储引擎自动优化创建,不能人为干预是否创建 Hash 索引;Memory 默认使用 Hash 索引,但也支持 BTREE 索引。
FULLTEXT索引
- MySQL 5.6 之前,只有 MyISAM 支持 FULLTEXT 全文本索引,本质是对文本的内容进行分词,进行搜索,只限于 CHAR、VARCHAR、TEXT 列,对整个列进行,不支持局部前缀索引。它的出现是为了解决 WHERE name LIKE “%word%" 这类针对文本的模糊查询效率较低的问题。5.6 之后,InnoDB 也支持 FULLTEXT。
空间索引
- MyISAM 表支持空间索引,在 MySQL5.7 版本以后,InnoDB 还引入了空间索引,对 GIS 数据的支持,即可以存储和查询空间数据。
3.2.7 常见存储引擎的适用场景
如果应用是以 select 和 insert 为主,只有很少的 update、delete,并且对事务的完整性、并发性要求不是很高,使用 MyISAM 很合适。
如果应用对事务的完整性有比较高的要求,在并发条件下要求数据的一致性,数据操作除了 select 和 insert 外,还有很多 update、delete,使用 InnoDB 比较合适。
在需要快速定位记录时,Memory 可以提供极快的访问。但对表的大小有限制,太大的表无法缓存到内存,通常用在更新不太频繁的小表,快速得到访问结果。
4. 索引的原理
4.1 索引分类标准
按数据结构分类可分为:B+tree索引、B-Tree索引、Hash索引、Full-text索引、空间索引。
按物理存储分类可分为:聚簇索引、二级索引(辅助索引)。
按字段特性分类可分为:主键索引、普通索引、唯一索引、前缀索引。
按字段个数分类可分为:单列索引、联合索引(复合索引、组合索引)。
4.2 聚簇索引
聚簇索引的每个叶子节点存储了一行完整的表数据,叶子节点间按id列递增连接,可以方便地进行顺序检索。
也就是说,聚集索引的B+树中的叶子节点存放的是整张表的行记录数据。一个表最多只能有一个聚集索引,Innodb通过主键聚集数据,如果没有定义主键, Innodb会选择非空的唯一索引代替。如果没有这样的索引,innodb会隐式的定义一个主键来作为聚集索引。
4.3 二级索引
非聚集索引索引的叶子节点并不包含行记录的全部数据,而是存储相应行数据的聚集索引键,即主键。Innodb里非主键索引又被称为二级索引、辅助索引, 均属于非聚集索引。
4.4 回表
当通过辅助索引来查询数据时,InnoDB存储引擎会遍历辅助索引找到主键,然后再通过主键在聚集索引中找到完整的行记录数据,这个过程称为回表。
4.5 索引覆盖
如果 select 后面查询的字段都可以从这个索引的树中获取,而不用回表,这种情况一般可以说是用到了覆盖索引。
4.6 索引下推
ICP,index condition pushdown,MySQL 5.6 引入的一个优化,它可以在索引遍历过程中,对索引中包含的字段先做判断,直接在InnoDB存储引擎层过滤掉 不满足条件的记录,减少回表次数。
- 索引下推发生在组合索引
- 索引下推触发条件必须 sql 会回表,否则下推没有意义
4.7 前缀索引
对字符类型字段的前几个字符或对二进制类型字段的前几个bytes建立的索引,而不是在整个字段上建索引。
前缀索引可以建立在类型为char、varchar、binary、varbinary的列上,可以大大减少索引占用的存储空间,也能提升索引的查询效率。但在Order by 和 group by 时无法使用。
前缀索引的长度跟存储引擎相关,对于 MyISAM 表,索引的前缀长度可以达到 1000 字节长;对于 InnoDB 表,索引的前缀长度最长是 767 字节。
4.8 联合索引
建立在多个列上的索引被称为联合索引,又叫复合索引、组合索引。需要理解联合索引的有序性和最左前缀原理,否则会导致索引失效。
- 减少开销:建一个联合索引(col1,col2,col3),实际相当于建了(col1),(col1,col2),(col1,col2,col3)三个索引。每多一个索引,都会增加写操作的开销和磁盘空间的开销。对于大量数据的表,使用联合索引会大大的减少开销。
- 覆盖索引:对联合索引(col1,col2,col3),如果有如下的sql: select col1,col2,col3 from test where col1=1 and col2=2。那么MySQL可以直接通过遍历索引取得数据,而无需回表,这减少了很多的随机io操作。减少io操作,特别的随机io其实是dba主要的优化策略。所以,在真正的实际应用中,覆盖索引是主要的提升性能的优化手段之一。
- 筛选效率高:索引列越多,通过索引筛选出的数据越少。有1000W条数据的表,有如下sql: select from table where col1=1 and col2=2 and col3=3,假设假设每个条件可以筛选出10%的数据,如果只有单值索引,那么通过该索引能筛选出1000W*10%=100w条数据,然后再回表从100w条数据中找到符合col2=2 and col3=3的数据,然后再排序,再分页;如果是联合索引,通过索引筛选出1000w*10%*10%*10%=1w。
- 有序:索引本身是有顺序的,当要对索引字段排序时,那么查询到的数据天然就是有顺序的,减少了排序的开销。
4.9 Hash索引、BTREE索引、B+TREE索引
4.9.1 Hash索引
Hash 索引结构的特殊性,其检索效率非常高,索引的检索可以一次定位,不像B-Tree 索引需要从根节点到枝节点,最后才能访问到页节点这样多次的IO访问,所以 Hash 索引的查询效率要远高于 B-Tree 索引。
虽然 Hash 索引效率高,但是 Hash 索引本身由于其特殊性也带来了很多限制,主要有以下这些。
1. Hash 索引仅仅能满足 = , IN 和 <=>(表示NULL安全的等价) 查询,不能使用范围查询
- 由于 Hash 索引比较的是进行 Hash 运算之后的 Hash值,所以它只能用于等值的过滤,不能用于基于范围的过滤,因为经过相应的 Hash算法处理 之后的 Hash 值的大小关系,并不能保证和Hash运算前完全一样。 对于BTREE索引,使用>、<、>=、<=、BETWEEN、!=或者<>,或者like(pattern不以通配符开始),都可以使用相关列上的索引。
2. 优化器不能使用 Hash 索引来加速order by操作
- 由于 Hash 索引中存放的是经过 Hash 计算之后的 Hash值,而且Hash值的大小关系并不一定和 Hash运算前的键值完全一样,所以数据库无法利用 索引的数据来避免任何排序运算。
3. Hash 索引不能利用部分索引键查询,只能使用整个关键字搜索一行
- 对于组合索引,Hash 索引在计算 Hash 值的时候是组合索引键合并后再一起计算 Hash 值,而不是单独计算 Hash值,所以通过组合索引的前面一 个或几个索引键进行查询的时候,Hash 索引也无法被利用。
4. Hash 索引依然需要回表扫描
- Hash 索引只包含哈希值和行指针,而不存储字段值。
- Hash 索引是将索引键通过 Hash 运算之后,将 Hash运算结果的 Hash值和所对应的行指针信息存放于一个 Hash 表中,由于不同索引键可能存在相同 Hash 值,所以即使取满足某个 Hash 键值的数据的记录条数,也无法从 Hash索引中直接完成查询,还是要通过访问表中的实际数据进行相应的比较,并得到相应的结果。
5. Hash索引遇到大量Hash值相等的情况后性能并不一定就会比B-Tree索引高
- 选择性比较低的索引键,如果创建 Hash 索引,那么将会存在大量记录指针信息存于同一个Hash值相关联。这样要定位某一条记录时就会非常麻 烦,会浪费多次表数据的访问,而造成整体性能低下。
- 如果哈希冲突很多的话,一些索引维护操作的代价也会很高。例如,如果在某个选择性很低(哈希仲突很多)的列上建立哈希索引,那么当从表中删 除一行时,存储引擎需要遍历对应哈希值的链表中的每一行,找到并删除对应行的引用,冲突越多,代价越大。
由于范围查询是MySQL数据库查询中常见的场景,Hash表不适合做范围查询,它更适合做等值查询。另外Hash表还存在Hash函数选择和Hash值冲突等问题。因 此,B+tree索引要比Hash表索引有更广的适用场景。
4.9.2 BTREE索引
B树是一个平衡多路查找树,B为Blanced,是为磁盘等外存储设备设计的一种平衡查找树,形状偏“瘦高”。
- 关键字集合分布在整棵树中
- 任何一个关键字出现且只出现在一个结点中
- 搜索有可能在非叶子节点结束
- 其搜索性能等价于在关键字全集内做一次二分查找
InnoDB存储引擎中有页(Page)的概念,页是其磁盘管理的最小单位。InnoDB存储引擎中默认每个页的大小为16KB,可通过参数innodb_page_size将页的 大小设置为4K、8K、16K。
MySQL16KB
mysql> show variables like 'innodb_page_size';
+------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+-------+
| innodb_page_size | 16384 |
+------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)而系统一个磁盘块的存储空间往往没有这么大,因此InnoDB每次申请磁盘空间时都会是若干地址连续磁盘块来达到页的大小16KB。
InnoDB在把磁盘数据读入到磁盘时会以页为基本单位,在查询数据时如果一个页中的每条数据都能有助于定位数据记录的位置,这将会减少磁盘I/O次数,提高查询效率。
4.9.2.1 页分裂
B-Tree为了维护索引有序性,在插入新值的时候需要做必要的维护,当插入入一个新记录时,如果新插入的ID值在数据中间,就需要逻辑上挪动后面的数据,空出位置。
而更糟的情况是,所在的数据页已经满了,根据 B-Tree 的算法,这时候需要申请一个新的数据页,然后挪动部分数据过去。这个过程称为页分裂。在这种情况下,性能就会受影响。不是按顺序插入,而是随机插入,产生很多移动数据,也会导致页分裂。
页分裂会产生表空间碎片
- 影响数据页的利用率。原本放在一个页的数据,现在分到两个页中,整体空间利用率降低大约 50%。
- 可能导致查询扫描的IO成本提升,效率查询降低;
当然有分裂就有合并。
当我们删除某一行记录时,其实MySQL只是把此行记录标记为了“可复用”,但磁盘大小是不会变的,所以通过delete表中记录是达不到回收表空间的。这 些被标记为“可复用”而没有使用的空间看起来就像是“空洞”,当相邻两个页由于删除了数据,利用率很低之后,可将数据页做合并。即通过 optimize table 来重组文件。
产生表空间碎片的其他常见的原因
- 记录被Delete,且原空间无法复用;
- 记录被Update(通常出现在变长字段中),原空间无法复用;
4.9.2.2 自增主键 VS 非自增主键
自增主键的插入数据模式,正符合了递增插入的场景。每次插入一条新记录,都是追加操作,都不涉及到挪动其他记录,也不会触发叶子节点的分裂。而有 业务逻辑的字段做主键,由于每次插入主键的值近似于随机,则会产生很多移动数据,页分裂,进而造成了大量的碎片,大大影响性能。
4.9.2.3 为什么不用其他查询性能更好的树?
传统来搜索的平衡叉树有很多,如 AVL 树,红树等。这些树在般情况下查询性能常好,但当数据常的时候它们就能为了。原因当数据量常时,内存不够,无法将全部数据读入内存,部分数据只能存放在磁盘上,只有需要的数据才加载到内存中。般内存访问的时间约为50 ns,磁盘在10 ms 左右。速度相差了近 5 个数量级,磁盘读取时间远远超过了数据在内存中较的时间。这说明程序部分时间会阻塞在磁盘 IO 上。而B树数据存储在各个节点上,那么每次读入内存的信息就比较有效,一次查询可能产生很多次IO,那么我们如何减少磁盘 IO 次数,于是有B+树。
4.9.3 B+TREE树
B+树是在B树基础上的一种优化,使其更适合实现存储索引结构,InnoDB存储引擎就是用B+Tree实现其索引结构,形状偏“矮胖”。
B+树相对于B树有几点不同:
- 非叶子节点只存储键值信息。
- 所有叶子节点之间都有一个链指针。
- 数据记录都存放在叶子节点中。
总结一下这种结构的优点:
- B+ 树的层级更少:相较于 B 树 B+ 每个非叶子节点存储的关键字数更多,树的层级更少所以查询数据更快
- B+ 树查询速度更稳定:B+ 所有关键字数据地址都存在叶子节点上,所以每次查找的次数都相同所以查询速度要比B树更稳定
- B+ 树支持范围查询:叶子节点的关键字从小到大有序排列,左边结尾数据都会保存右边节点开始数据的指针
- B+ 树天然具备排序功能:B+ 树所有的叶子节点数据构成了一个有序链表,在查询大小区间的数据时候更方便,数据紧密性很高,缓存的命中率也会比B树高
- B+ 树全节点遍历更快:B+ 树遍历整棵树只需要遍历所有的叶子节点即可,而不需要像 B 树一样需要对每一层进行遍历,这有利于数据库做全表扫描。
InnoDB存储引擎中页的大小为16KB,一般表的主键类型为INT(占用4个字节)或BIGINT(占用8个字节),指针类型也一般为4或8个字节,也就是说一个页(B+Tree中的一个节点)中大概存储16KB/(8B+8B)=1K个键值(因为是估值,为方便计算,这里的K取值为〖10〗^3)。也就是说一个深度为 3 的 B+Tree 索引可以维护10^3 * 10^3 * 10^3 = 10亿条记录。
实际情况中每个节点可能不能填充满,因此在数据库中,B+Tree 的高度一般都在 2~4 层。MySQL的 InnoDB 存储引擎在设计时是将根节点常驻内存的,也就是说查找某一键值的行记录时最多只需要 1~3 次磁盘 I/O 操作。
5. 索引的实践
这里所有的实践都是基于 MySQL 5.7.26 版本的 InnoDB 存储引擎!!!
在实操之前,需要确定当前使用的 MySQL 版本,因为不同的版本,对同一问题的表现不同。
mysql> SELECT VERSION();
+-----------+
| VERSION() |
+-----------+
| 5.7.26 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)查看当前数据库支持的存储引擎,
mysql> show engines;
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys | YES | YES | YES |
| MRG_MYISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
| BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO |
| CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | YES | MyISAM storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO| NO | NO |
| FEDERATED | NO | Federated MySQL storage engine | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)查看当前数据库默认的存储引擎,
mysql> show variables like '%storage_engine%';
+----------------------------------+--------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+----------------------------------+--------+
| default_storage_engine | InnoDB |
| default_tmp_storage_engine | InnoDB |
| disabled_storage_engines | |
| internal_tmp_disk_storage_engine | InnoDB |
+----------------------------------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)查看具体某个表使用的存储引擎,
mysql> show table status from sakila where name="actor" \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** Name: actorEngine: InnoDB Version: 10Row_format: Dynamic Rows: 200Avg_row_length: 81Data_length: 16384Max_data_length: 0Index_length: 16384Data_free: 0Auto_increment: 201Create_time: 2023-08-06 17:15:38Update_time: 2023-08-06 17:16:33 Check_time: NULLCollation: utf8mb4_general_ci Checksum: NULLCreate_options:Comment:
1 row in set (0.00 sec)查看样本库的数据量,
+----------------------------+----------+------------+
| Tables | Columns | Total Rows |
+----------------------------+----------+------------+
| actor | 4 | 200 |
| actor_info | 4 | 200 |
| address | 9 | 603 |
| category | 3 | 16 |
| city | 4 | 600 |
| country | 3 | 109 |
| customer | 9 | 599 |
| customer_list | 9 | 599 |
| film | 13 | 1000 |
| film_actor | 3 | 5462 |
| film_category | 3 | 1000 |
| film_list | 8 | 1000 |
| film_text | 3 | 1000 |
| inventory | 4 | 4581 |
| language | 3 | 6 |
| nicer_but_slower_film_list | 8 | 1000 |
| payment | 7 | 16044 |
| rental | 7 | 16044 |
| sales_by_film_category | 2 | 16 |
| sales_by_store | 3 | 2 |
| staff | 11 | 2 |
| staff_list | 8 | 2 |
| store | 4 | 2 |
+----------------------------+----------+------------+5.1 索引设计原则
5.1.1 设计原则
1. 搜索的索引列,不一定是所要选择的列。
最适合索引的列是出现在where子句里的列,或者连接子句中的列,而不是出现在select关键字后的选择列表中的列。
2. 使用唯一索引
考虑列中值的分布,索引中列的基数越大,索引的效果越好。
3. 使用短索引
如果对字符串列进行索引,应该指定一个前缀长度,只要有可能就应该这么做。
这样能够节省大量索引空间,也可能会是查询更快,较小的索引涉及的磁盘ID较少,较短的值比较起来更快。
对于较短的键值,索引高速缓存中的块能容纳更多的键值,这样,MySQL可以在内存中容纳更多的值,就增加了找到行而不用读取索引中较多块的可能性。
4. 利用最左前缀
在创建一个n列的索引时,实际是创建了MySQL可利用的n个索引,多列索引可起几个索引的作用,可利用索引中最左边的列集来匹配行。
5. 不要过度索引
索引不是越多越好,每个额外的索引都要占用磁盘空间,并降低写操作性能。
在修改表的内容时,索引必须进行更新,有时可能需要重构。索引越多,花的时间越长。如果一个索引很少使用或从不使用,就不必要地减缓表的 修改速度。
MySQL在生成一个执行计划时,要考虑各个索引,也要花费时间。创建多余的索引给查询优化带来了更多的工作。
索引太多,也可能会使MySQL选择不到所要使用的最好索引,只保持所需的索引有利于查询优化。
6. InnoDB表记录默认会按照一定顺序保存,
如果有明确定义的主键,则按照主键顺序保存。
如果没有主键,但有唯一索引,就按照唯一索引的顺序保存。
如果既没有主键,也没有唯一索引,表中会自动生成一个内部列,按照这个列的顺序保存。按照主键或者内部列进行的访问最快,所以InnoDB表尽量自己指定主键。
当表中同时有几个列都是唯一的,都可以作为主键时,要选择最常访问条件的列作为主键,提高查询效率。
InnoDB表的普通索引都会保存主键的键值,所以主键要尽可能选择较短的数据类型,减少索引的磁盘占用,提高索引的缓存效果。
5.1.2 应该创建索引的列
在经常使用在WHERE子句中的列上面创建索引,加快条件的判断速度。
在经常需要搜索的列上,可以加快搜索的速度
在作为主键的列上,强制该列的唯一性和组织表中数据的排列结构
在经常用在连接(JOIN)的列上,这些列主要是一外键,可以加快连接的速度
在经常需要根据范围(<,<=,=,>,>=,BETWEEN,IN)进行搜索的列上创建索引,因为索引已经排序,其指定的范围是连续的
在经常需要排序(order by)的列上创建索引,因为索引已经排序,这样查询可以利用索引的排序,加快排序查询时间。
5.2 索引问题
mysql> desc rental;
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| customer_id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | MUL | NULL | |
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show index from rental;
+--------+------------+---------------------+--------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+--------+------------+---------------------+--------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| rental | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | rental_id | A | 16008 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| rental | 1 | idx_fk_inventory_id | NULL | | BTREE | |
| rental | 1 | idx_fk_customer_id | NULL | | BTREE | |
| rental | 1 | idx_fk_staff_id | NULL | | BTREE | |
| rental | 1 | idx_rental_date | NULL | | BTREE | |
| rental | 1 | idx_rental_date | NULL | | BTREE | |
| rental | 1 | idx_rental_date | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+--------+------------+---------------------+--------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
7 rows in set (0.01 sec)mysql> desc payment;
+--------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| payment_id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| customer_id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| staff_id | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| rental_id | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| amount | decimal(5,2) | NO | | NULL | |
| payment_date | datetime | NO | | NULL | |
| last_update | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+--------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> show index from payment;
+---------+------------+--------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+---------+------------+--------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| payment | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | payment_id | A | 16086 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | idx_fk_staff_id | 1 | staff_id | A | 2 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | idx_fk_customer_id | 1 | customer_id | A | 599 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | fk_payment_rental | 1 | rental_id | A | 16044 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+---------+------------+--------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> desc film_text;
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| film_id | smallint(6) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| title | varchar(255) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| description | text | YES | | NULL | |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> show index from film_text;
+-----------+------------+-----------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------
+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-----------+------------+-----------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| film_text | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | film_id | A | 1000 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| film_text | 1 | idx_title_description | 1 | title | NULL | 1000 | NULL | NULL | | FULLTEXT | | |
| film_text | 1 | idx_title_description | 2 | description | NULL | 1000 | NULL | NULL | YES | FULLTEXT | | |
+-----------+------------+-----------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)5.2.1 能够使用索引的典型场景
1. 匹配全值,对索引中所有列都指定具体值,即是对索引中的所有列都有等值匹配的条件。
// type const
mysql> explain select * from rental where rental_date='2005-05-25 17:22:10' and inventory_id = 373 and customer_id = 343 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: rental partitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_fk_inventory_id,idx_fk_customer_id,idx_rental_date key: idx_rental_datekey_len: 10ref: const,const,const rows: 1filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)2. 匹配值的范围查询,对索引的值能进行范围查找。
mysql> explain select * from rental where customer_id >= 373 and customer_id < 400 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: rental partitions: NULLtype: range
possible_keys: idx_fk_customer_idkey: idx_fk_customer_id key_len: 2ref: NULL rows: 718filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)3. 匹配最左前缀,仅仅使用索引中的最左边列进行查找。最左匹配原则算是MySQL中BTREE索引使用的首要原则。
mysql> alter table payment add index idx_payment_date(payment_date, amount, last_update); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0mysql> explain select * from payment where payment_date = '2006-02-14 15:16:03' and last_update = '2006-02-15 22:12:32' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_payment_datekey: idx_payment_date key_len: 5ref: const rows: 182filtered: 10.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)//
mysql> explain select * from payment where amount = 3.98 and last_update = '2006-02-15 22:12:32' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 1.00Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)4. 仅仅对索引进行查询,查询的列都在索引的字段中时,查询的效率更高,即索引覆盖。
mysql> explain select last_update from payment where payment_date = '2006-02-14 15:16:03' and amount = 3.98 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_payment_datekey: idx_payment_date key_len: 8ref: const,const rows: 8filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using index
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)5. 匹配列前缀,仅仅使用索引中的第一列,且只包含索引第一列的开头一部分进行查找,即前缀索引。
mysql> create index idx_title_desc_part on film_text(title(10), description(20)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0mysql> explain select title from film_text where title like 'AFRICAN%' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: film_text partitions: NULLtype: range
possible_keys: idx_title_desc_part,idx_title_description key: idx_title_desc_partkey_len: 42ref: NULL rows: 1filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)6. 能够实现索引匹配部分精确,而其他部分进行范围匹配。
mysql> explain select inventory_id from rental where rental_date = '2006-02-14 15:16:03' and customer_id >= 300 and customer_id <= 400 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: rentalpartitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_fk_customer_id,idx_rental_date key: idx_rental_datekey_len: 5ref: const rows: 182filtered: 16.85Extra: Using where; Using index
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)7. 如果列名是索引,那么使用 column_name is null 就会使用索引。
mysql> explain select * from payment where rental_id is null \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: fk_payment_rentalkey: fk_payment_rental key_len: 5ref: const rows: 1filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)8. MySQL 5.6引入了索引下推特性,进一步优化了查询。索引下推,就是把操作下放,某些情况下的条件过滤操作下放到操作引擎。(同第2点)
5.2.2 存在索引但是不能使用索引的典型场景
1.以%开头的like查询不能使用BTREE索引
- 因为BTREE索引的结构,%开头的查询无法利用索引,一般推荐使用全文索引解决类似的全文检索问题。
- 或者考虑利用利用InnoDB表都是聚簇表的特点,采取一种轻量级别的解决方式。
- 一般情况下,索引都会比表小,扫描索引要比扫描表更快(某些特殊情况下,索引比表大,不在本例讨论范围内),而InnoDB表上的二级索引实际上存储除了字段的值,还有主键,理想的访问方式应该是首先扫描二级索引获得满足条件like匹配的主键列表(这是一个子查询的索引覆盖),之后根据主键回表检索记录,这样访问就避开了全表扫描产生的大量IO请求。
mysql> explain select * from actor where last_name like '%NI%' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 200filtered: 11.11 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)2. 数据类型出现隐式转换时,不会使用索引,特别常见的是字符串,where条件要把字符常量值引号引起来。
mysql> explain select * from actor where last_name = 1 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: idx_actor_last_name key: NULLkey_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 200filtered: 10.00 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 3 warnings (0.01 sec)mysql> explain select * from actor where last_name = '1' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_actor_last_name key: idx_actor_last_namekey_len: 182ref: const rows: 1filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)3. 复合索引条件下,查询条件不包含索引列的最左边部分,不满足最左原则,不会使用复合索引。
mysql> explain select * from payment where amount = 3.98 and last_update = '2006-02-15 22:12:32' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 1.00Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)4. MySQL估计使用索引比全表扫描更慢,则不使用索引。在查询时,筛选性越高,越容易使用到索引,筛选性越低,越不容易使用索引。
mysql> select count(*) from film_text where title like 's%';
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 119 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select * from film_text where title like 's%' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: film_text partitions: NULLtype: range
possible_keys: idx_title_desc_part,idx_title_description key: idx_title_desc_partkey_len: 42ref: NULL rows: 119filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> update film_text set title = concat('s', title);
Query OK, 1000 rows affected (0.08 sec)
Rows matched: 1000 Changed: 1000 Warnings: 0mysql> explain select * from film_text where title like 's%' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: film_text partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: idx_title_desc_part,idx_title_description key: NULLkey_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 1000filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)5. 用or分割开的条件,如果or前的条件中的列有索引,后面的列没有索引,涉及的索引不会被用到。 因为or后面的条件列没有索引,后面的查询会走全表扫描,在存在全表扫描的情况下,没必要多一次索引扫描增加IO访问。
mysql> explain select * from payment where customer_id = 203 or amount = 3.96 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: idx_fk_customer_idkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 10.15 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)6.索引列上有计算
mysql> explain select * from payment where payment_id = 1 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: const
possible_keys: PRIMARYkey: PRIMARYkey_len: 2ref: const rows: 1filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)mysql> explain select * from payment where payment_id + 1 = 2 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)7.索引列使用了函数
mysql> explain select * from actor where last_name like 'PE%' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: range
possible_keys: idx_actor_last_namekey: idx_actor_last_name key_len: 182ref: NULL rows: 6filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)mysql> explain select * from actor where substr(last_name, 1, 2) = 'PE' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 200filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)8. Not in 和 not exists
mysql> explain select * from actor where last_name in ('WAHLBERG', 'DAVIS') \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: range
possible_keys: idx_actor_last_namekey: idx_actor_last_name key_len: 182ref: NULL rows: 5filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select * from actor where last_name not in ('WAHLBERG', 'DAVIS') \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: idx_actor_last_name key: NULLkey_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 200filtered: 97.50 Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)9. Order by的坑(见4.3)
5.3 优化 order by
mysql> desc customer;
+-------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| customer_id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| store_id | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| first_name | varchar(45) | NO | | NULL | |
| last_name | varchar(45) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| email | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| address_id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| active | tinyint(1) | NO | | 1 | |
| create_date | datetime | NO | | NULL | |
| last_update | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+-------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> show index from customer;
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| customer | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | customer_id | A | 599 | NULL |
NULL | | BTREE | | |
| customer | 1 | idx_fk_store_id | 1 | store_id | A | 2 | NULL |
NULL | | BTREE | | |
| customer | 1 | idx_fk_address_id | 1 | address_id | A | 599 | NULL |
NULL | | BTREE | | |
| customer | 1 | idx_last_name | 1 | last_name | A | 599 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> desc payment;
+--------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| payment_id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| customer_id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| staff_id | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| rental_id | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| amount | decimal(5,2) | NO | | NULL | |
| payment_date | datetime | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| last_update | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+--------------+----------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> show index from payment;
+---------+------------+--------------------+--------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+---------+------------+--------------------+--------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| payment | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | payment_id | A | 16086 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | idx_fk_staff_id | 1 | staff_id | A | 2 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | idx_fk_customer_id | 1 | customer_id | A | 599 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | fk_payment_rental | 1 | rental_id | A | 16044 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | idx_payment_date | 1 | payment_date | A | 15815 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | idx_payment_date | 2 | amount | A | 15864 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| payment | 1 | idx_payment_date | 3 | last_update | A | 16038 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+---------+------------+--------------------+--------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)5.3.1 MySQL中的两种排序方式
1. Index方式
- 通过有序索引顺序扫描直接返回有序数据,这种方式在执行计划分析时,Extra列为Using index,不需要额外的排序,操作效率较高;
2. Filesort方式
- 通过对返回的数据进行排序,就是Filesort排序,所有不是通过索引直接返回排序结果的排序都叫FileSort排序。FileSort排序并不代表通过磁盘文件进行排序,而只是说明进行了一个排序操作,至于排序操作是否使用了磁盘文件或临时表等,则取决于MySQL服务器对排序参数的设置和需要排序数据的大小。
- Filesort是通过相应的排序算法,将取得的数据在 sort_buffer_size 系统变量设置的内存排序区中进行的排序,如果内存装载不下,它就会将磁盘上的数据进行分块,再对各个数据块进行排序,然后将各个块合并成有序的结果集。sort_buffer_size设置的排序区是每个线程独占的,所以同一时刻,MySQL中存在多个sort buffer排序区。
mysql> explain select customer_id from customer order by store_id \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: customer partitions: NULLtype: index
possible_keys: NULLkey: idx_fk_store_id key_len: 1ref: NULL rows: 599filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using index
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select * from customer order by store_id \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: customer partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 599filtered: 100.00Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)5.3.2 order by 优化目标
尽量使用Index方式排序返回有序数据,避免使用FileSort方式额外排序。
5.3.3 优化原则
排序字段加索引,尽量使用索引排序,如果这里使用ID排序的话,因为ID是索引字段,天生就具备有序的特性,所以这种情况都不需要放到sort buffer中去 额外进行排序操作。
where 条件和 order by 使用相同的索引,并且 order by 的顺序和索引顺序相同,并且 order by 的字段都是升序或者都是降序,否则肯定需要额外的排序操 作,出现Filesort。
只 select 需要的字段,避免非必要的字段查询,只 select 需要的字段,这点非常重要。
- 因为查询的字段较多可能导致数据会超出sort buffer的容量,超出之后就需要用到磁盘临时文件,排序的性能会很差。
- 当select的字段大小总和>max_length_for_sort_data,排序算法会将全字段排序改为 rowid 排序,增加一次回表查询。
- 全字段排序,一次扫描,直接输出结果集;
- rowid 排序,两次扫描,第一次条件取出排序字段和行指针,在 sort buffer 排序好后,根据行指针回表读取。回表会有大量随机 IO。
对于联合索引,尽可能在索引列上完成排序操作,遵照索引建的最左前缀。
- order by 语句使用索引最左前列;
- 使用 where 子句与 order by 子句条件列组合满足索引最左前列;
- where 子句中如果出现索引的范围查询(即explain中出现range)会导致 order by 索引失效。
select * from tablename order by key_part1, key_part2,...;
select * from tablename where key_part1 = 1 order by key_part1 desc, key_part2 desc;
select * from tablename order by key_part1 desc, key_part2 desc;select * from tablename order by key_part1 desc, key_part2 asc; // order by ASCDESC
select * from tablename order by where key2 = 1 order by key1; // order by
select * from tablename order by key1, key2; // order by5.3.4 order by的哪些情况可以走索引
1. 满足最左匹配原则
order by后面的条件,也要遵循联合索引的最左匹配原则。除了遵循最左匹配原则之外,有个非常关键的地方是,后面还是加了 limit 关键字,如果不加它索引会失效。
mysql> explain select * from payment order by payment_date \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 100.00Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select * from payment order by payment_date limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: index
possible_keys: NULLkey: idx_payment_date key_len: 12ref: NULL rows: 10filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select * from payment order by payment_date, amount limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: index
possible_keys: NULLkey: idx_payment_date key_len: 12ref: NULL rows: 10filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)// order by
mysql> explain select * from payment order by payment_date, last_update limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 100.00Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select * from payment order by payment_date, amount, last_update limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: index
possible_keys: NULLkey: idx_payment_date key_len: 12ref: NULL rows: 10filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)2. 配合where一起使用
order by还能配合where一起遵循最左匹配原则。
mysql> explain select * from payment where payment_date = '2006-02-14 15:16:03' order by amount \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_payment_datekey: idx_payment_datekey_len: 5ref: const rows: 182filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)mysql> explain select * from payment where payment_date = '2006-02-14 15:16:03' order by last_update \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_payment_datekey: idx_payment_date key_len: 5ref: const rows: 182filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition; Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)3. order by后面如果包含了联合索引的多个排序字段,相同的排序依然能命中索引。
mysql> explain select * from payment order by payment_date desc, amount desc limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: index
possible_keys: NULLkey: idx_payment_date key_len: 12ref: NULL rows: 10filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)4. 如果某个联合索引字段,在where和order by中都有,依然能命中索引。
mysql> explain select * from payment where payment_date = '2006-02-14 15:16:03' order by payment_date, amount \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_payment_datekey: idx_payment_date key_len: 5ref: const rows: 182filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)5.3.5 order by的哪些情况下不走索引
1. 没加where或limit。如果order by语句中没有加where或limit关键字,该sql语句将不会走索引。(见4.3.1.1.4的第一种)
2. 对不同的索引做order by。前面介绍的基本都是联合索引,这一个索引的情况。但如果对多个索引进行order by,索引也会失效。
mysql> explain select * from payment order by payment_date, amount, customer_id limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 100.00Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)3. 不满足最左匹配原则
mysql> explain select * from payment order by amount desc limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 100.00Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)4. 不同的排序
mysql> explain select * from payment order by payment_date asc, amount desc limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 100.00Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)5.3.6 order by 小结
对于 KEY a_b_c(a, b, c)
1. order by 能使用索引最左前缀(必须要带 where 或 limit);
2. 如果where使用索引的最左前缀定义为常量,则 order by 能使用索引
- where a = const order by b, c
- where a = const and b = const order by c
- where a = const and b > const order by c
- where a = const and b > const order by b, c
3. 不能使用索引进行排序
- order by a asc, b desc, c desc // 排序不一致
- where g = const order by b, c // 丢失索引a
- where a = const order by c // 丢失索引b
- where a = const order by a, d // d不是索引的一部分
- where a in (...) order by b, c // 对于排序来说,多个相等条件也是范围查询
/**
where a = const and b > const order by b , c // Using file sort b, c
where a = const and b > const order by c // using filesort b order by b c
*/
mysql> explain select * from payment where payment_date = '2006-02-14 15:16:03' and amount > 1 order by amount, last_update \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: range
possible_keys: idx_payment_datekey: idx_payment_date key_len: 8ref: NULL rows: 105filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select * from payment where payment_date = '2006-02-14 15:16:03' and amount > 1 order by last_update \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: range
possible_keys: idx_payment_datekey: idx_payment_date key_len: 8ref: NULL rows: 105filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition; Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/356463167
5.4 优化 group by
默认情况下,MySQL对所有 group by col1, col2, ...的字段进行排序,原理和在查询中指定 order by col1, col2, ...类似。所以,如果显式包括一个包含相同列的order by子句,对MySQL的实际执行性能没有什么影响。
如果查询保包括 group by,但用户想避免排序的消耗,可以指定 order by null 禁止排序。
// group by filesort
mysql> explain select first_name, count(*) from actor group by first_name \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 200filtered: 100.00Extra: Using temporary; Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select first_name, count(*) from actor group by first_name order by null \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: actor partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 200filtered: 100.00Extra: Using temporary
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)5.5 优化分页查询
一般分页查询,通过创建索引覆盖能比较好地提高性能。一个常见又很头疼的分页场景是“limit 1000, 20”,MySQL排序出前1020条记录后,仅仅需要返回第1001到1020条记录,前1000条记录都会被抛弃,查询和排序的代码非常高。
mysql> desc film;
+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| film_id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| title | varchar(128) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| description | text | YES | | NULL | |
| release_year | year(4) | YES | | NULL | |
| language_id | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| original_language_id | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| rental_duration | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | | 3 | |
| rental_rate | decimal(4,2) | NO | | 4.99 | |
| length | smallint(5) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| replacement_cost | decimal(5,2) | NO | | 19.99 | |
| rating | enum('G','PG','PG-13','R','NC-17') | YES | | G | |
| special_features | set('Trailers','Commentaries','Deleted Scenes','Behind the Scenes') | YES | | NULL | |
| last_update | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
13 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> show index from film;
+-------+------------+-----------------------------+--------------+----------------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+-----------------------------+--------------+----------------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| film | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | film_id | A | 1000 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| film | 1 | idx_title | 1 | title | A | 1000 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| film | 1 | idx_fk_language_id | 1 | language_id | A | 1 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| film | 1 | idx_fk_original_language_id | 1 | original_language_id | A | 1 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+-----------------------------+--------------+----------------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select film_id, description from film order by title limit 50, 5 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: film partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 1000filtered: 100.00Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select a.film_id, a.description from film a inner join (select film_id from film order by title limit 50, 5) b on a.film_id = b.film_id \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: PRIMARY table: <derived2>partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 55filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL*************************** 2. row *************************** id: 1select_type: PRIMARY table: apartitions: NULLtype: eq_ref
possible_keys: PRIMARYkey: PRIMARYkey_len: 2ref: b.film_id rows: 1filtered: 100.00Extra: NULL*************************** 3. row *************************** id: 2select_type: DERIVED table: filmpartitions: NULLtype: index
possible_keys: NULLkey: idx_title key_len: 514ref: NULL rows: 55filtered: 100.00 Extra: Using index
3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)//limit
mysql> explain select * from payment order by rental_id desc limit 410, 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: NULLkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 16086filtered: 100.00Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)// last_page_record rental_id 4241
mysql> select * from payment order by rental_id desc limit 410, 10;
+------------+-------------+----------+-----------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+
| payment_id | customer_id | staff_id | rental_id | amount | payment_date | last_update |
+------------+-------------+----------+-----------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+
| 5830 | 214 | 2 | 15639 | 2.99 | 2005-08-23 08:03:25 | 2006-02-15 22:14:15 |
| 15100 | 563 | 2 | 15638 | 3.99 | 2005-08-23 07:54:54 | 2006-02-15 22:22:07 |
| 4686 | 172 | 2 | 15637 | 2.99 | 2005-08-23 07:53:38 | 2006-02-15 22:13:44 |
| 10304 | 380 | 2 | 15636 | 2.99 | 2005-08-23 07:50:46 | 2006-02-15 22:17:21 |
| 107 | 4 | 2 | 15635 | 1.99 | 2005-08-23 07:43:00 | 2006-02-15 22:12:30 |
| 15454 | 576 | 1 | 15634 | 0.99 | 2005-08-23 07:34:18 | 2006-02-15 22:22:32 |
| 13402 | 497 | 2 | 15633 | 0.99 | 2005-08-23 07:31:10 | 2006-02-15 22:20:17 |
| 1668 | 60 | 1 | 15632 | 0.99 | 2005-08-23 07:30:26 | 2006-02-15 22:12:45 |
| 2552 | 93 | 2 | 15631 | 2.99 | 2005-08-23 07:30:23 | 2006-02-15 22:12:57 |
| 15559 | 580 | 1 | 15630 | 6.99 | 2005-08-23 07:29:13 | 2006-02-15 22:22:39 |
+------------+-------------+----------+-----------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+
10 rows in set (0.02 sec)// limit m,n limit n
mysql> explain select * from payment where rental_id < 15630 order by rental_id desc limit 10 \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLEtable: payment partitions: NULLtype: range
possible_keys: fk_payment_rentalkey: fk_payment_rental key_len: 5ref: NULL rows: 8043filtered: 100.00Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)5.6 优化 or 条件
对于含有or的查询子句,要利用索引,or之间的每个条件列都必须用到索引。如果没有索引,则应该考虑增加索引。
Using union,对 or 的各个字段分别查询后做了一次 union。
当在建有复合索引的列上面做or时,不能用到索引。
5.7 SQL HINT
在SQL语句中加入人为的提示,达到优化操作的目的。
- use index:提供希望 MySQL 参考的索引列表,就可以让 MySQL 不再考虑其他可用的索引,起到建议的作用。
- ignore index:让 MySQL 忽略一个或者多个索引。
- force index:强制使用一个特定的索引,这是 MySQL 留给用户的一个自行选择执行计划的权利。
6. SQL优化步骤
1.通过 show status 命令了解各种SQL的执行频率
mysql> show global status where Variable_name = 'Com_select' or Variable_name = 'Com_insert' or Variable_name = 'Com_update' or Variable_name = 'Com_delete';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Com_delete | 0 |
| Com_insert | 1017 |
| Com_select | 14 |
| Com_update | 0 |
+---------------+-------+4 rows in set (0.00 sec)2. 定位执行效率较低的SQL
通过慢查询日志定位
慢查询日志在查询结束后才记录,在应用反映执行效率出现问题时查询慢查询日志并不能定位问题,可以使用 show processlist命令查看当前 MySQL 在进行 的线程,包括线程状态、是否锁表等,可以实时查看 SQL 的执行情况,同时对锁表进行优化。
3. explain 分析执行计划
mysql> explain select sum(amount) from customer a, payment b where 1=1 and a.customer_id = b.customer_id and email = 'JANE.BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org' \G
*************************** 1. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLE table: apartitions: NULLtype: ALL
possible_keys: PRIMARYkey: NULL key_len: NULLref: NULL rows: 599filtered: 10.00 Extra: Using where*************************** 2. row *************************** id: 1select_type: SIMPLE table: bpartitions: NULLtype: ref
possible_keys: idx_fk_customer_idkey: idx_fk_customer_id key_len: 2ref: sakila.a.customer_id rows: 26filtered: 100.00 Extra: NULL
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) id列,为执行的顺序,每个号码,表示一趟独立的查询,id列越大执行优先级越高,id相同则从上往下执行,id为NULL最后执行。
id列,为执行的顺序,每个号码,表示一趟独立的查询,id列越大执行优先级越高,id相同则从上往下执行,id为NULL最后执行。
select_type 列,查询分为简单查询(SIMPLE)和复杂查询(PRIMARY)。复杂查询分为三类:简单子查询、派生表(from语句中的子查询)、union查询。
- SIMPLE:简单查询。不包含子查询和union
- PRIMARY:复制查询中的最外层的select
- DERIVED:包含在 from 子句中的子查询。MySQL会将结果存放在一个临时表中,也称为派生表
- SUBQUERY:包含在 select 中的子查询(不在 from 子句中)
- UNION:在 union 中的第二个和随后的 select
- UNIONRESULT:从union临时表检索结果的result
- union结果总是放在一个匿名临时表中,临时表不在SQL中出现,因此它的id是NULL。

table列,这一列表示 explain 的一行正在访问哪个表(用户操作的用户表,输出结果集的表)。
- 当 from 子句中有子查询时,table 列是格式,表示当前查询依赖 id=N 的查询,于是先执行 id=N 的查询。
- <derivedN>: 派生表,由id等于N的语句产生
- <subqueryN>: 由子查询物化产生的表,由id等于N的语句产生
- 当有 union 时,UNION RESULT 的 table 列的值为<union1,2>,1和2表示参与 union 的 select 行 id。
- <unionM,N>: UNION得到的结果表。
type列,这一列表示MySQL在表中找到所需行的方式,即访问类型。MySQL决定如何查找表中的行,查找数据行记录的大概范围。
依次从最优到最差分别为:system > const > eq_ref > ref > range > index > ALL
性能优化的目标,得保证查询至少达到range级别,最好达到ref。
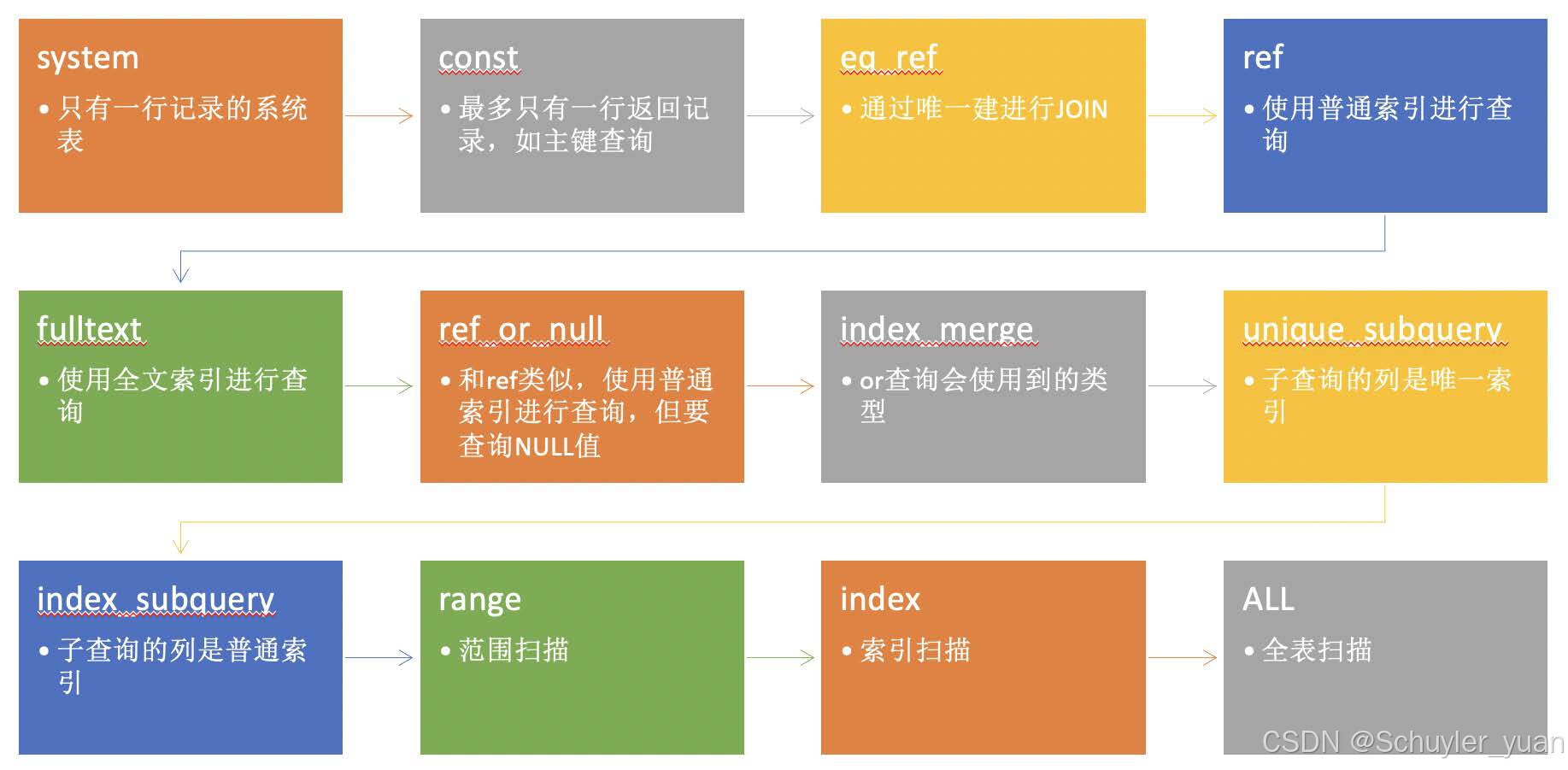
possible_keys列,显示可能应用在这张表中的索引,一个或多个。查询涉及到的字段上若存在索引,则该索引将被列出,但不一定被查询实际使用。
key列,实际使用的索引。如果为NULL,则没有使用索引。explain 时可能出现 possible_keys 有列,而 key 显示 NULL 的情况,这种情况是因为表中数据 不多,mysql认为索引对此查询帮助不大,选择了全表查询。
key_len列,
ref列,这一列显示了在key列记录的索引中,表查找值所用到的列或常量,常见的有:const(常量),字段名,指的是 “=”号后面的东西。
row列,检查的行数,读取的行数越少越好。
filtered列,表示存储引擎返回的数据在server层(及其他过滤条件)过滤后,剩下多少满足查询的记录数量的比例。
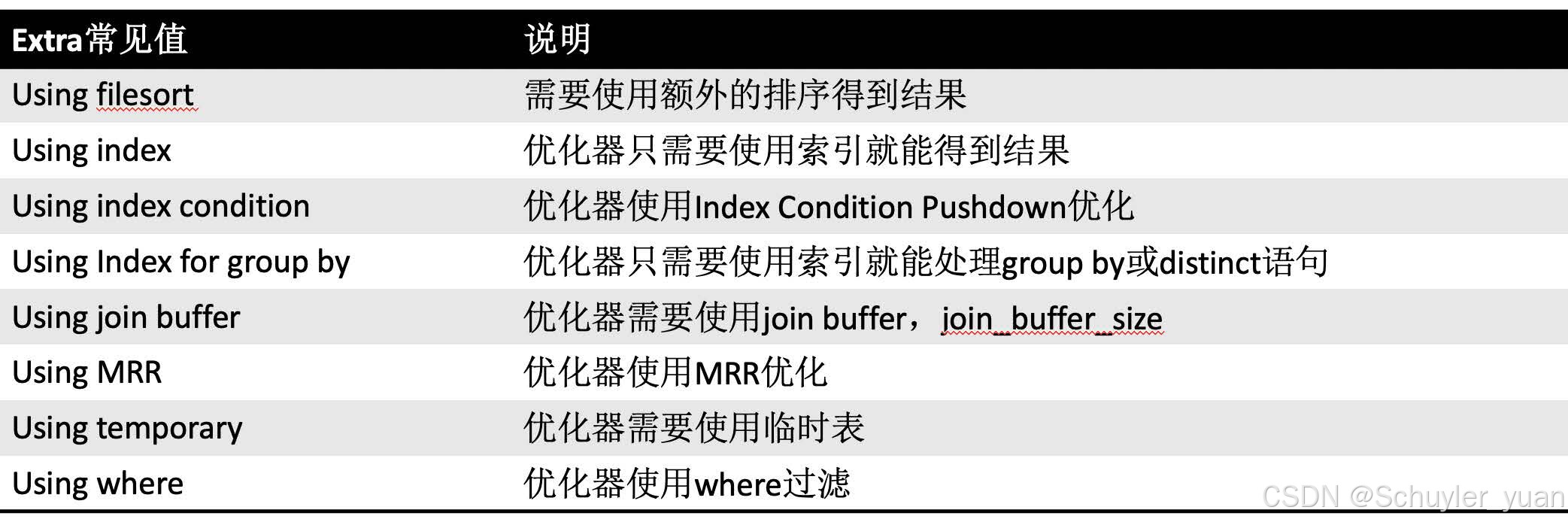
Extra列,这一列展示的是额外信息,
- Using index: 直接访问索引就足够获取到所需要的数据,不需要回表,就是覆盖索引扫描。
- Using where:查询的where条件列未被索引覆盖,表示优化器除了利用索引来加速访问之外,还需要根据索引回表查询数据。
- Using filesort:mysql 会对结果使用一个外部索引排序,而不是按索引次序从表里读取行。此时mysql会并保存排序关键字和行指针,然后排序关键字并按顺序检索行信息。这种无法利用索引完成的排序操作称为“文件排序”。这种情况下一般也是要考虑使用索引来优化的。
- NULL:查询的列未被索引覆盖,查询的where条件走了索引
- Using index condition: 索引下推优化,查询的列不完全被索引覆盖,条件使用索引,是一个范围
- Using temporary:mysql需要创建一张临时表来处理查询。
4. 通过show profile分析SQL
通过profile,可以更清楚地了解SQL执行过程。show profile能够在SQL优化时帮助我们了解时间都耗费在哪了。
查看当前MySQL是否支持profile,
mysql> select @@have_profiling;
+------------------+
| @@have_profiling |
+------------------+
| YES |
+------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)默认profiling是关闭的,需要打开session级别的profiling,
mysql> select @@profiling;
+-------------+
| @@profiling |
+-------------+
| 0 |
+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec) mysql> set profiling=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)执行sql后,show profiles 看到当前SQL的 QueryID 是 1,
mysql> select count(*) from payment;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 16044 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)mysql> show profiles;
+----------+------------+------------------------------+
| Query_ID | Duration | Query |
+----------+------------+------------------------------+
| 1 | 0.00616900 | select count(*) from payment |
+----------+------------+------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)查看执行过程中线程的每个状态和消耗的时间,
mysql> show profile for query 1;
+----------------------+----------+
| Status | Duration |
+----------------------+----------+
| starting | 0.000209 |
| checking permissions | 0.000029 |
| checking permissions | 0.000006 |
| Opening tables | 0.000048 |
| init | 0.000069 |
| System lock | 0.000018 |
| optimizing | 0.000014 |
| statistics | 0.000081 |
| preparing | 0.000053 |
| executing | 0.000004 |
| Sending data | 0.005517 |
| end | 0.000026 |
| query end | 0.000016 |
| closing tables | 0.000018 |
| freeing items | 0.000033 |
| cleaning up | 0.000028 |
+----------------------+----------+16 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)Sending data 状态表示 MySQL 线程开始访问数据行并把结果返回给客户端,不仅仅是返回结果给客户端。由于该状态时,MySQL线程需要做大量的磁盘IO, 所以经常是整个查询中耗时最长的状态。
为了更清晰地看到排序结果,查看INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROFILING表,并按照时间desc排序,
mysql> select STATE, SUM(DURATION) as Total_R,
ROUND(100*SUM(DURATION) /
(
select SUM(DURATION) from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROFILING where QUERY_ID = 1
), 2) as Pct_R,
count(*) as Calls,
SUM(DURATION) / COUNT(*) as "R/Call"
from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROFILING
where QUERY_ID = 1 group by STATE order by Total_R desc;
+----------------------+----------+-------+-------+--------------+
| STATE | Total_R | Pct_R | Calls | R/Call |
+----------------------+----------+-------+-------+--------------+
| Sending data | 0.005517 | 89.43 | 1 | 0.0055170000 |
| starting | 0.000209 | 3.39 | 1 | 0.0002090000 |
| statistics | 0.000081 | 1.31 | 1 | 0.0000810000 |
| init | 0.000069 | 1.12 | 1 | 0.0000690000 |
| preparing | 0.000053 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.0000530000 |
| Opening tables | 0.000048 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.0000480000 |
| checking permissions | 0.000035 | 0.57 | 2 | 0.0000175000 |
| freeing items | 0.000033 | 0.53 | 1 | 0.0000330000 |
| cleaning up | 0.000028 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.0000280000 |
| end | 0.000026 | 0.42 | 1 | 0.0000260000 |
| System lock | 0.000018 | 0.29 | 1 | 0.0000180000 |
| closing tables | 0.000018 | 0.29 | 1 | 0.0000180000 |
| query end | 0.000016 | 0.26 | 1 | 0.0000160000 |
| optimizing | 0.000014 | 0.23 | 1 | 0.0000140000 |
| executing | 0.000004 | 0.06 | 1 | 0.0000040000 |
+----------------------+----------+-------+-------+--------------+rows in set, 2 warnings (0.01 sec)获取到最消耗时间的线程状态后,MySQL支持进一步选择 all、cpu、block io、context switch、page faults等明细类型来查看MySQL在使用什么资源上耗费了过高的时间。
下面选择查看CPU的消耗时间,能够发现Sending data状态下,时间主要消耗在CPU上了。
mysql> show profile cpu for query 1;
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+
| Status | Duration | CPU_user | CPU_system |
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+
| starting | 0.000209 | 0.000162 | 0.000024 |
| checking permissions | 0.000029 | 0.000026 | 0.000003 |
| checking permissions | 0.000006 | 0.000005 | 0.000001 |
| Opening tables | 0.000048 | 0.000046 | 0.000002 |
| init | 0.000069 | 0.000067 | 0.000002 |
| System lock | 0.000018 | 0.000017 | 0.000001 |
| optimizing | 0.000014 | 0.000011 | 0.000002 |
| statistics | 0.000081 | 0.000081 | 0.000002 |
| preparing | 0.000053 | 0.000050 | 0.000002 |
| executing | 0.000004 | 0.000003 | 0.000001 |
| Sending data | 0.005517 | 0.005432 | 0.000016 |
| end | 0.000026 | 0.000010 | 0.000016 |
| query end | 0.000016 | 0.000015 | 0.000002 |
| closing tables | 0.000018 | 0.000016 | 0.000001 |
| freeing items | 0.000033 | 0.000017 | 0.000016 |
| cleaning up | 0.000028 | 0.000027 | 0.000001 |
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+16 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)5. MySQL 5.6 提供了对SQL 的跟踪trace,通过trace文件可以了解优化器选择A执行计划而不选择B执行计划,帮助我们更好地理解优化器的行为。 打开 trace,设置格式为json,
mysql> set OPTIMIZER_TRACE='enabled=on',END_MARKERS_IN_JSON=on;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)执行查询,
mysql> select sum(amount) from customer a, payment b where 1=1 and a.customer_id = b.customer_id and email = 'JANE.BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org';
+-------------+
| sum(amount) |
+-------------+
| 100.72 |
+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)检查 INFORMATION_SCHEMA.OPTIMIZER_TRACE,就能知道 MySQL 怎么执行 SQL 的。
{"steps": [{"join_preparation": {"select#": 1,"steps": [{"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select sum(`b`.`amount`) AS `sum(amount)` from `customer` `a` join `payment` `b` where ((1 = 1) and (`a`.`customer_id` = `b`.`customer_id`) and (`a`.`email` = 'JANE. BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org'))"}]}},{"join_optimization": {"select#": 1,"steps": [{"condition_processing": {"condition": "WHERE","original_condition": "((1 = 1) and (`a`.`customer_id` = `b`.`customer_id`) and (`a`.`email` = 'JANE.BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org'))","steps": [{"transformation": "equality_propagation","resulting_condition": "((1 = 1) and (`a`.`email` = 'JANE.BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org') and multiple equal(`a`.`customer_id`, `b`.`customer_id`))"},{"transformation": "constant_propagation","resulting_condition": "((1 = 1) and (`a`.`email` = 'JANE.BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org') and multiple equal(`a`.`customer_id`, `b`.`customer_id`))"},{"transformation": "trivial_condition_removal","resulting_condition": "((`a`.`email` = 'JANE.BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org') and multiple equal (`a`.`customer_id`, `b`.`customer_id`))"}]}},{"substitute_generated_columns": {}},{"table_dependencies": [{"table": "`customer` `a`","row_may_be_null": false,"map_bit": 0,"depends_on_map_bits": []},{"table": "`payment` `b`","row_may_be_null": false,"map_bit": 1,"depends_on_map_bits": []}]},{"ref_optimizer_key_uses": [{"table": "`customer` `a`","field": "customer_id","equals": "`b`.`customer_id`","null_rejecting": false},{"table": "`payment` `b`","field": "customer_id","equals": "`a`.`customer_id`","null_rejecting": false}]},{"rows_estimation": [{"table": "`customer` `a`","table_scan": {"rows": 599,"cost": 5}},{"table": "`payment` `b`","table_scan": {"rows": 16086,"cost": 97}}]},{"considered_execution_plans": [{"plan_prefix": [],"table": "`customer` `a`","best_access_path": {"considered_access_paths": [{"access_type": "ref","index": "PRIMARY","usable": false,"chosen": false},{"rows_to_scan": 599,"access_type": "scan","resulting_rows": 59.9,"cost": 124.8,"chosen": true}]},"condition_filtering_pct": 100,"rows_for_plan": 59.9,"cost_for_plan": 124.8,"rest_of_plan": [{"plan_prefix": ["`customer` `a`"],"table": "`payment` `b`","best_access_path": {"considered_access_paths": [{"access_type": "ref","index": "idx_fk_customer_id","rows": 26.855,"cost": 1930.3,"chosen": true},{"rows_to_scan": 16086,"access_type": "scan","using_join_cache": true,"buffers_needed": 1,"resulting_rows": 16086,"cost": 192812,"chosen": false}]},"condition_filtering_pct": 100,"rows_for_plan": 1608.6,"cost_for_plan": 2055.1,"chosen": true}]},{"plan_prefix": [],"table": "`payment` `b`","best_access_path": {"considered_access_paths": [{"access_type": "ref","index": "idx_fk_customer_id","usable": false,"chosen": false},{"rows_to_scan": 16086,"access_type": "scan","resulting_rows": 16086,"cost": 3314.2,"chosen": true}]},"condition_filtering_pct": 100,"rows_for_plan": 16086,"cost_for_plan": 3314.2,"pruned_by_cost": true}]},{"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {"original_condition": "((`b`.`customer_id` = `a`.`customer_id`) and (`a`.`email` = 'JANE. BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org'))","attached_conditions_computation": [],"attached_conditions_summary": [{"table": "`customer` `a`","attached": "(`a`.`email` = 'JANE.BENNETT@sakilacustomer.org')"},{"table": "`payment` `b`","attached": null}]}},{"refine_plan": [{"table": "`customer` `a`"},{"table": "`payment` `b`"}]}]}},{"join_execution": {"select#": 1,"steps": []}}]
}6. 确定问题并采取相应的优化措施,比如全表扫描就需要对索引优化。
7. 最后
没有性能优化的“绝对真理”,而应该是在实际的业务场景下通过测试来验证你关于执行计划以及响应时间的假设,Trade-off balance。








