摘要
本文介绍了快速探索随机树(Rapidly-exploring Random Tree, RRT)算法在二维环境中的路径规划应用。RRT是一种随机采样算法,能够快速构建从起点到目标点的路径,特别适用于复杂环境中的机器人路径规划。通过在随机方向上扩展树结构,RRT算法能够高效避开障碍物并找到一条可行路径。
理论
RRT算法通过不断随机采样空间中的节点,并尝试将当前树扩展到这些节点,逐步构建一条从起点到目标点的路径。其关键步骤包括:
-
随机采样:在环境中随机采样一个点,作为树扩展的方向。
-
树扩展:尝试从当前树的一个节点向采样点扩展,生成一个新节点。
-
避障检测:检查新节点是否与障碍物发生碰撞,如果发生则放弃该节点。
-
路径生成:不断重复上述步骤,直到树包含了目标点,从而生成一条可行路径。
实验结果
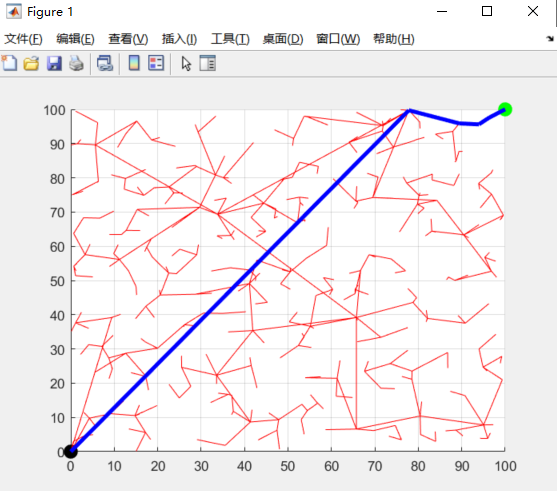
实验使用RRT算法在二维环境中进行路径规划测试,结果显示算法能够快速生成路径并有效避开环境中的障碍物。以下是实验的主要发现:
-
路径生成速度:RRT能够在较短时间内生成路径,适合实时应用。
-
避障性能:算法能够在复杂障碍环境中找到可行路径,但生成的路径可能不够平滑。
-
优化潜力:通过对路径进行后续优化处理(如RRT*),可以进一步改善路径的平滑性和总长度。
部分代码
% Define map and parameters
mapSize = [0, 50, 0, 50]; % Map size [xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]
startPos = [5, 5]; % Start position
goalPos = [45, 45]; % Goal position
maxStep = 2; % Maximum step size% Initialize RRT
nodes = startPos; % Start node
edges = []; % Edge list% Main RRT loop
while norm(nodes(end,:) - goalPos) > 1% Random samplingrandPoint = [rand * (mapSize(2) - mapSize(1)), rand * (mapSize(4) - mapSize(3))];% Find nearest node[~, nearestIdx] = min(vecnorm(nodes - randPoint, 2, 2));nearestNode = nodes(nearestIdx, :);% Extend towards the random pointdirection = (randPoint - nearestNode) / norm(randPoint - nearestNode);newNode = nearestNode + maxStep * direction;% Collision check (assume no obstacles for simplicity)if newNode(1) >= mapSize(1) && newNode(1) <= mapSize(2) && ...newNode(2) >= mapSize(3) && newNode(2) <= mapSize(4)nodes = [nodes; newNode];edges = [edges; nearestIdx, size(nodes, 1)];end% Plot current stateplot(nodes(:,1), nodes(:,2), 'bo'); % Plot nodeshold on;plot([nodes(edges(:,1),1), nodes(edges(:,2),1)]', ...[nodes(edges(:,1),2), nodes(edges(:,2),2)]', 'k-'); % Plot edgesplot(goalPos(1), goalPos(2), 'ro', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'r'); % Plot goalpause(0.1);
end% Final path plotting
plot([nodes(end,1), goalPos(1)], [nodes(end,2), goalPos(2)], 'r-', 'LineWidth', 2);
title('2D RRT Path Planning');
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
grid on;
参考文献
❝
LaValle, S. M. (1998). Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees: A New Tool for Path Planning. Technical Report, Iowa State University.
Karaman, S., & Frazzoli, E. (2010). Incremental Sampling-Based Algorithms for Optimal Motion Planning. Robotics: Science and Systems VI.
Liu, J. (2024). Algorithms for Randomized Path Planning in Complex Environments. Springer.





