1.函数指针数组 2.转移表 3.回调函数
1.函数指针数组
存放函数指针的数组
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int add(int x, int y)
{return x + y;
}
int sub(int x, int y)
{return x - y;
}int main()
{int (*p1)(int x, int y) = add;int (*p2)(int x, int y) = sub;//在这里p1与p2的类型相同我们可以把其放在数组int (*p[4])(int, int) = { add,sub };//这里[4]代表函数指针数组大小可以存放4个函数指针。printf("%d\n",p[0](20, 30));printf("%d\n", p[1](20, 30));return 0;
}

2.转移表
函数指针数组的应用
首先使用数组的方式实现一个简易的计算功能
void meau()
{printf(" 开始选择 \n");printf("**** 1.add 2.sub ****\n");printf("**** 3.mul 4.div ****\n");printf("**** 0.exit ****\n");printf(" \n");}
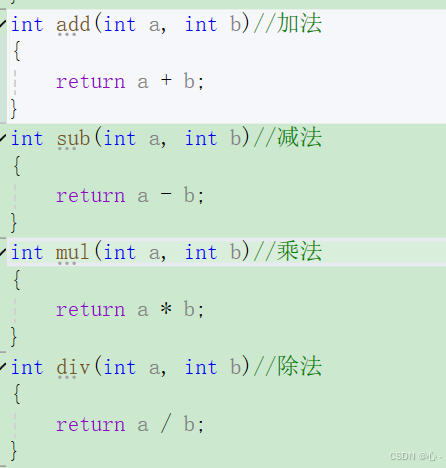
int add(int a, int b)//加法
{return a + b;
}
int sub(int a, int b)//减法
{return a - b;
}
int mul(int a, int b)//乘法
{return a * b;
}
int div(int a, int b)//除法
{return a /b;
}
void calc(int(*p)(int a, int b))
{int a = 0; int b = 0; int c = 0;printf("请输入两个整数进行运算\n");scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);c = p(a, b);printf("运算结果=%d\n", c);
}
int main()
{int input = 1;
do{int a = 0; int b = 0; int c = 0;meau();scanf("%d", &input);switch(input){case 1:printf("请输入两个整数进行运算\n");scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);c = add(a, b);printf("运算结果=%d\n", c);break;case 2:printf("请输入两个整数进行运算\n");scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);c = sub(a, b);printf("运算结果=%d\n", c);break;case 3:printf("请输入两个整数进行运算\n");scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);c = mul(a, b);printf("运算结果=%d\n", c);break;case 4:printf("请输入两个整数进行运算\n");scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);c = div(a, b);printf("运算结果=%d\n", c);break;case 0:printf("退出计算\n"); break;default :printf("选择错误请重新选择/n"); break;}
} while (input);return 0;
}
用函数指针数组的方式实现一个转移的效果
void meau()
{printf(" 开始选择 \n");printf("**** 1.add 2.sub ****\n");printf("**** 3.mul 4.div ****\n");printf("**** 0.exit ****\n");printf(" \n");}
int add(int a, int b)//加法
{return a + b;
}
int sub(int a, int b)//减法
{return a - b;
}
int mul(int a, int b)//乘法
{return a * b;
}
int div(int a, int b)//除法
{return a / b;
}
void calc(int(*p)(int a, int b))
{int a = 0; int b = 0; int c = 0;printf("请输入两个整数进行运算\n");scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);c = p(a, b);printf("运算结果=%d\n", c);
}
int main()
{int input = 1;do{meau();scanf("%d", &input);switch (input){case 1:calc(add);break;case 2:calc(sub);break;case 3:calc(mul);break;case 4:calc(div);break;case 0:printf("退出计算\n");break;default:printf("选择错误请重新选择/n");break;}} while (input);return 0;
}

3.回调函数
回调函数就是⼀个通过函数指针调⽤的函数。
如果你把函数的指针(地址)作为参数传递给另⼀个函数,当这个指针被⽤来调⽤其所指向的函数时,被调⽤的函数就是回调函数。回调函数不是由该函数的实现⽅直接调⽤,⽽是在特定的事件或条件发⽣时由另外的⼀⽅调⽤的,⽤于对该事件或条件进⾏响应。
在上面转移表的实现中已经使用的回调函数接下来给诠释一下


在这里列如 int add(int x,int y)——到void calc(int(*p)(int a, int b))——c=p(a,b);
这就是一次回调函数的实现。
持续指针系列


)



