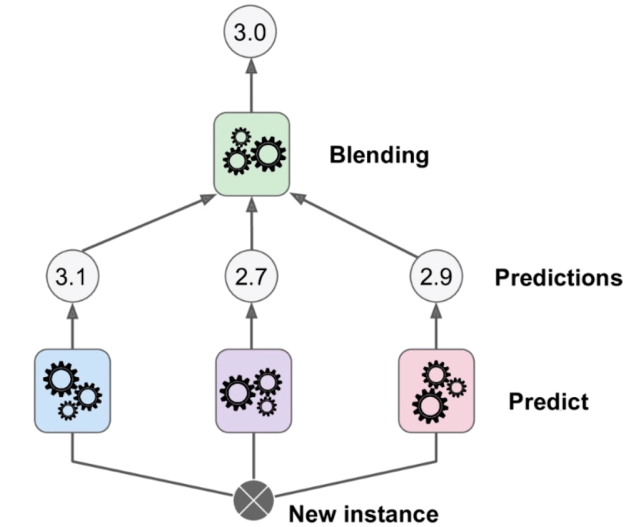
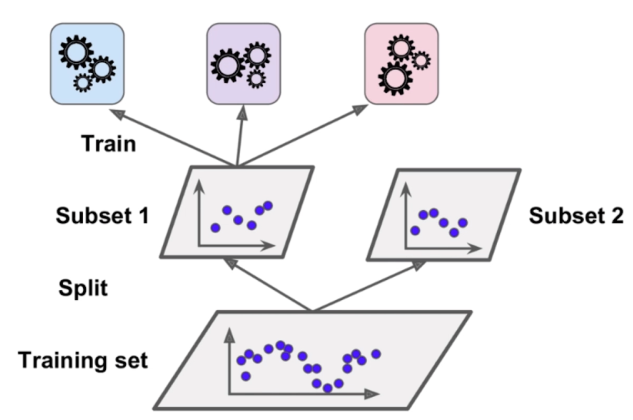
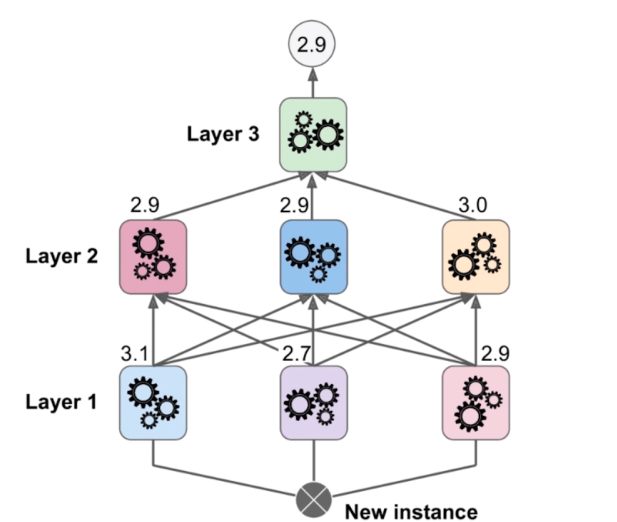
集成学习
生活中的集成学习:
买东西找别推荐
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
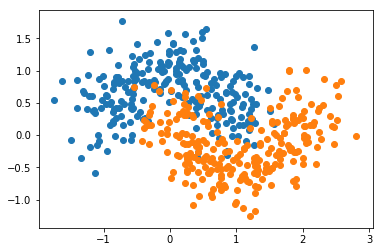
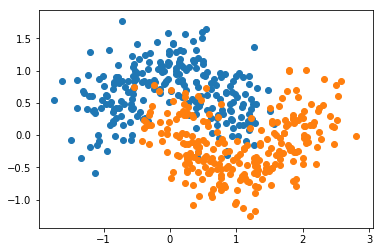
from sklearn import datasetsX, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.3, random_state=42)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionlog_clf = LogisticRegression()
log_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
log_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
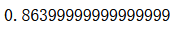
from sklearn.svm import SVCsvm_clf = SVC()
svm_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
svm_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
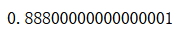
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierdt_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666)
dt_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
dt_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
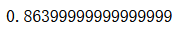
y_predict1 = log_clf.predict(X_test)
y_predict2 = svm_clf.predict(X_test)
y_predict3 = dt_clf.predict(X_test)
y_predict = np.array((y_predict1 + y_predict2 + y_predict3) >= 2, dtype='int')
y_predict[:10]
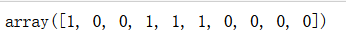
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_scoreaccuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
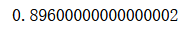
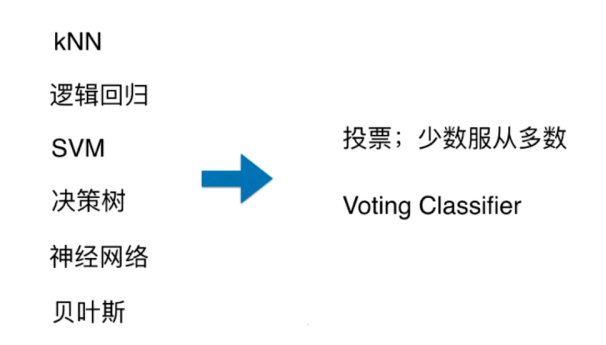
使用Voting Classifier
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifiervoting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), ('svm_clf', SVC()),('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666))],voting='hard')
voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
voting_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
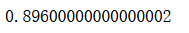
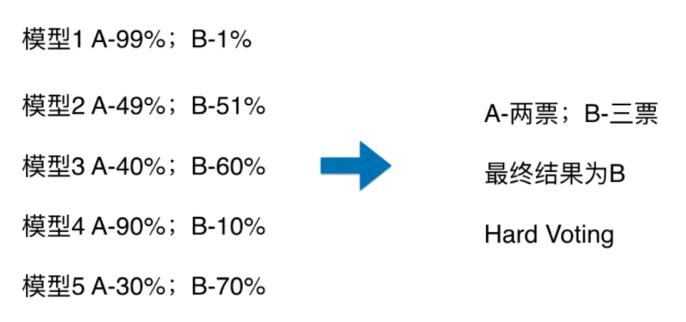
Soft Voting
Voting Classifier
更合理的投票,应该有权值
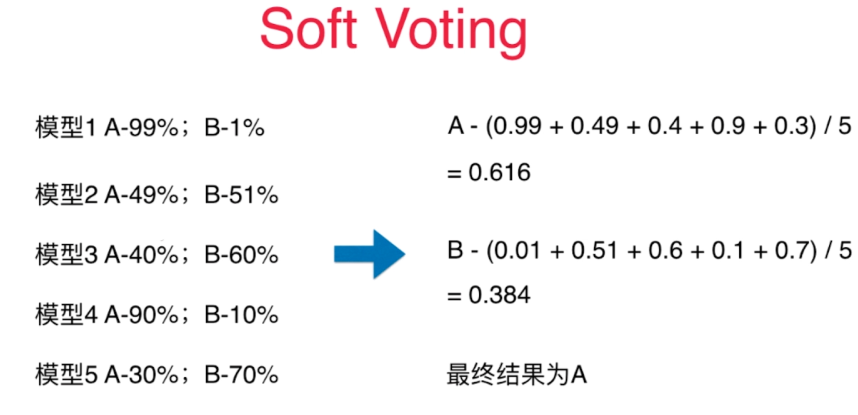
要求集合的每一个模型都能估计概率
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
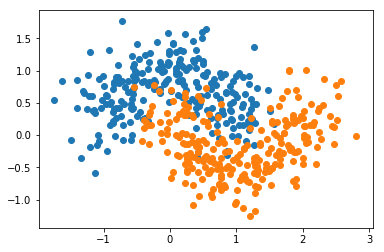
from sklearn import datasetsX, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.3, random_state=42)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
使用 Hard Voting Classifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifiervoting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), ('svm_clf', SVC()),('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666))],voting='hard')
voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
voting_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
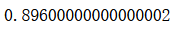
使用 Soft Voting Classifier
voting_clf2 = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), ('svm_clf', SVC(probability=True)),('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666))],voting='soft')
voting_clf2.fit(X_train, y_train)
voting_clf2.score(X_test, y_test)
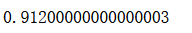
集成学习
虽然有很多机器学习方法,但是从投票的角度看,仍然不够多
创建更多的子模型!集成更多的子模型的意见。
子模型之间不能一致!子模型之间要有差异性
如何创建差异性?
每个子模型只看样本数据的一部分。
例如:一共有500个样本数据;每个子模型只看100个样本数据每个子模型不需要太高的准确率
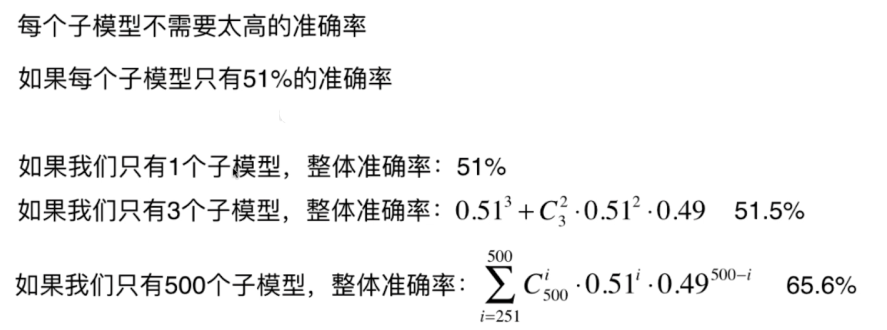

Bagging 和 Pasting
取样:放回取样,不放回取样
放回取样:Bagging 不放回取样:Pasting
Bagging 更常用
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasetsX, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.3, random_state=42)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
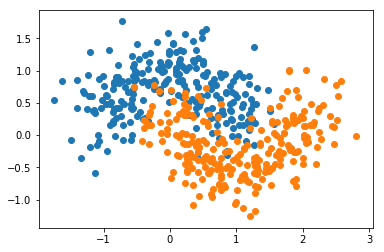
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
使用 Bagging
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifierbagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),n_estimators=500, max_samples=100,bootstrap=True)
bagging_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
bagging_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
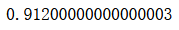
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifierbagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),n_estimators=5000, max_samples=100,bootstrap=True)
bagging_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
bagging_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
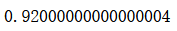
OOB Out-of-Bag
放回取样导致一部分样本很有可能没有取到
平均大约有37%的样本没有取到。
不使用测试数据集,而使用这部分没有取到的样本做测试/验证
生成数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasetsX, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.3, random_state=42)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
oob
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifierbagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),n_estimators=500, max_samples=100,bootstrap=True, oob_score=True)
bagging_clf.fit(X, y)
bagging_clf.oob_score_
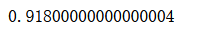
Bagging的思路极易并行化处理
%%time
bagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),n_estimators=500, max_samples=100,bootstrap=True, oob_score=True)
bagging_clf.fit(X, y)

%%time
bagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),n_estimators=500, max_samples=100,bootstrap=True, oob_score=True,n_jobs=-1)
bagging_clf.fit(X, y)

bootstrap_features
random_subspaces_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),n_estimators=500, max_samples=500,bootstrap=True, oob_score=True,max_features=1, bootstrap_features=True)
random_subspaces_clf.fit(X, y)
random_subspaces_clf.oob_score_
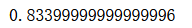
random_patches_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),n_estimators=500, max_samples=100,bootstrap=True, oob_score=True,max_features=1, bootstrap_features=True)
random_patches_clf.fit(X, y)
random_patches_clf.oob_score_
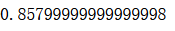
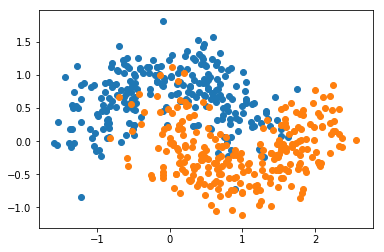
随机森林
Bagging
Base Estimator: Decision Tree
决策树在节点划分上,在随机的特征子集上寻找最优划分特征
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasetsX, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.3, random_state=666)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
随机森林
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierrf_clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500, oob_score=True, random_state=666, n_jobs=-1)
rf_clf.fit(X, y)
rf_clf.oob_score_
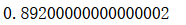
rf_clf2 = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500, max_leaf_nodes=16, oob_score=True, random_state=666, n_jobs=-1)
rf_clf2.fit(X, y)
rf_clf2.oob_score_
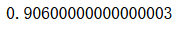
Extra-Trees
Bagging
Base Estimator: Decision Tree
决策树在节点划分上,使用随机的特征和随机的阈值
提供额外的随机性,抑制过拟合,但增大了bias
更快的训练速度
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifieret_clf = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=500, bootstrap=True, oob_score=True, random_state=666, n_jobs=-1)
et_clf.fit(X, y)
et_clf.oob_score_
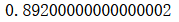
Boosting
集成多个模型
每个模型都在尝试增强(Boosting)整体的效果
Ada Boosting
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
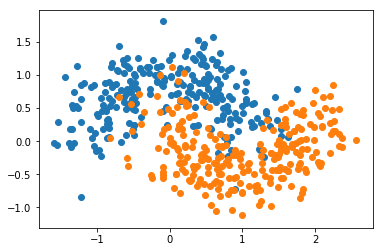
from sklearn import datasetsX, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.3, random_state=666)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=666)
AdaBoosting
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifierada_clf = AdaBoostClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2), n_estimators=500)
ada_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
ada_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
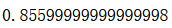
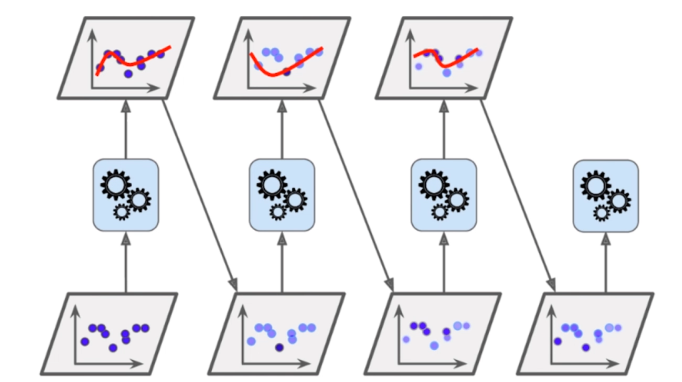
Gradient Boosting
训练一个模型m1,产生错误e1
针对e1训练第二个模型m2,产生错误e2
针对e2训练第三个模型m3,产生错误e3…
最终预测结果是:m1+m2+m3+…
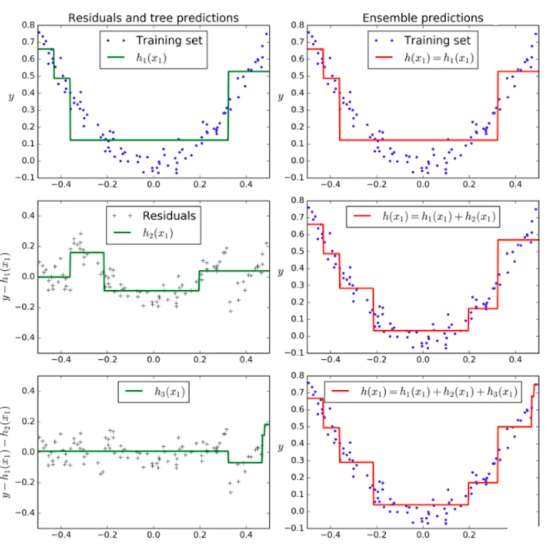
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifiergb_clf = GradientBoostingClassifier(max_depth=2, n_estimators=30)
gb_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
gb_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
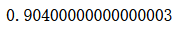
Stacking