
本文涉及前面文章内容:
1.C语言数据结构:二叉树堆的实现
本文内容如下:
- 1.堆排序的直接应用
- 2.堆排序的进阶使用
- 2.1用向上调整来建堆
- 2.2建队后的排序
- 方法一:取根节点重新建堆
- 方法二:建反堆
- 2.3用向下调整来建堆
- 3.建堆的时间复杂度的计算
- 4.TOP-K问题
1.堆排序的直接应用
之前我们在建堆时将删除写的是从头部数据的删除
如果我们将头部节点取下来
在不断删除头节点就可以进行排序了
写成代码:
void Test01()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);int arr[] = { 1,43,23,4,575,68,34,7,5,24,3,13,54, };for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int); i++){HPPush(&hp, arr[i]);}while (!HPEmpty(&hp)){printf("%d ", HPTop(&hp));HPPop(&hp);}printf("\n");HPDestroy(&hp);
}
之前的代码这里直接拿过来了:
void HPInit(HP* php)
{assert(php);php->a = NULL;php->size = php->capacity = 0;
}void HPDestroy(HP* php)
{assert(php);free(php->a);php->a = NULL;php->size = php->capacity = 0;
}void Swap(HPDataType* p1, HPDataType* p2)
{HPDataType tmp = *p1;*p1 = *p2;*p2 = tmp;
}void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){if (a[child] < a[parent]){Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}
}void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{assert(php);//空间扩容if (php->size == php->capacity){int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : php->capacity * 2;HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == 0){perror("realloc fail:");exit(1);}php->a = tmp;php->capacity = newcapacity;}php->a[php->size] = x;php->size++;AdjustUp(php->a, php->size - 1);
}void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent)
{int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < n){//用假设法判断哪个孩子较小if (a[child] > a[child + 1] && child + 1 < n){child = child + 1;}if (a[child] < a[parent]){Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{break;}}
}void HPPop(HP* php)
{assert(php);assert(php->size > 0);Swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[php->size - 1]);php->size--;AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, 0);
}
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php)
{assert(php);assert(php->size > 0);return php->a[0];
}
bool HPEmpty(HP* php)
{assert(php);return php->size == 0;
}
这样就完成了最基础的堆排序
但是这样有点太麻烦了
如果能直接将数组改变为堆,就会方便很多
2.堆排序的进阶使用
2.1用向上调整来建堆
这个最容易,我们直接通过遍历进行向上调整即可
void Test02()
{int arr[] = { 1,43,23,4,575,68,34,7,5,24,3,13,54, };int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){AdjustUp(arr, i);}
}
2.2建队后的排序
将堆建好后,如何将堆变为有序的呢?
一共有两种方法:
方法一:取根节点重新建堆
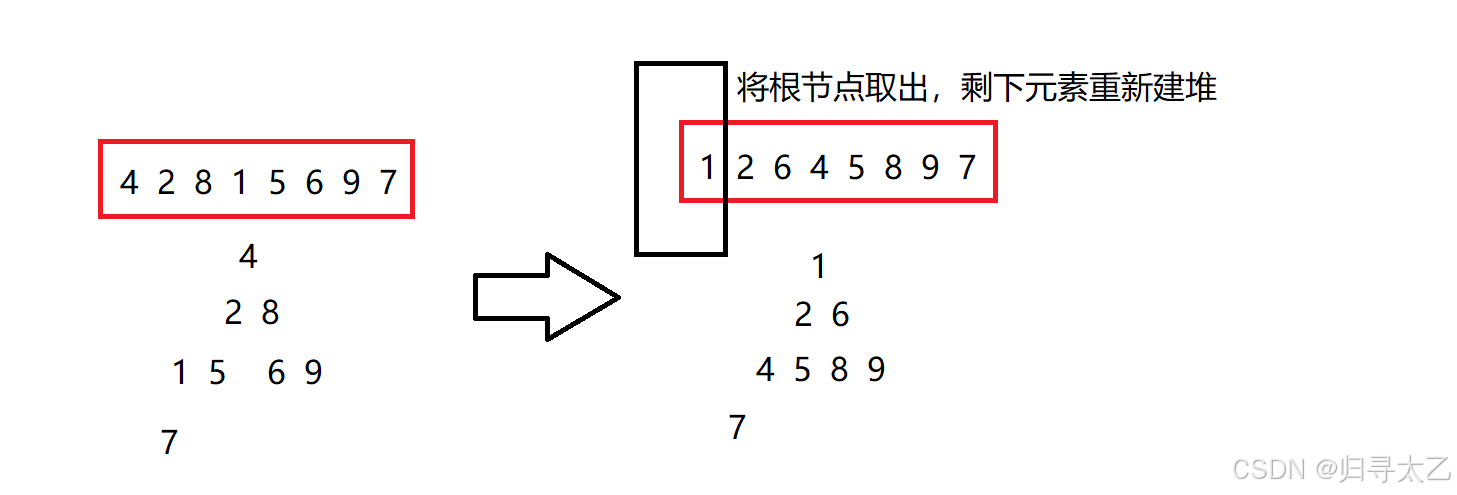
通过这样不断将首元素取出
其余元素重新建堆
通过重新调整再找新的跟节点,就能完成目的
但这样也就太麻烦了
方法二:建反堆
首尾元素交换就可以确定最小的数
剩下的继续交换重复来完成降序
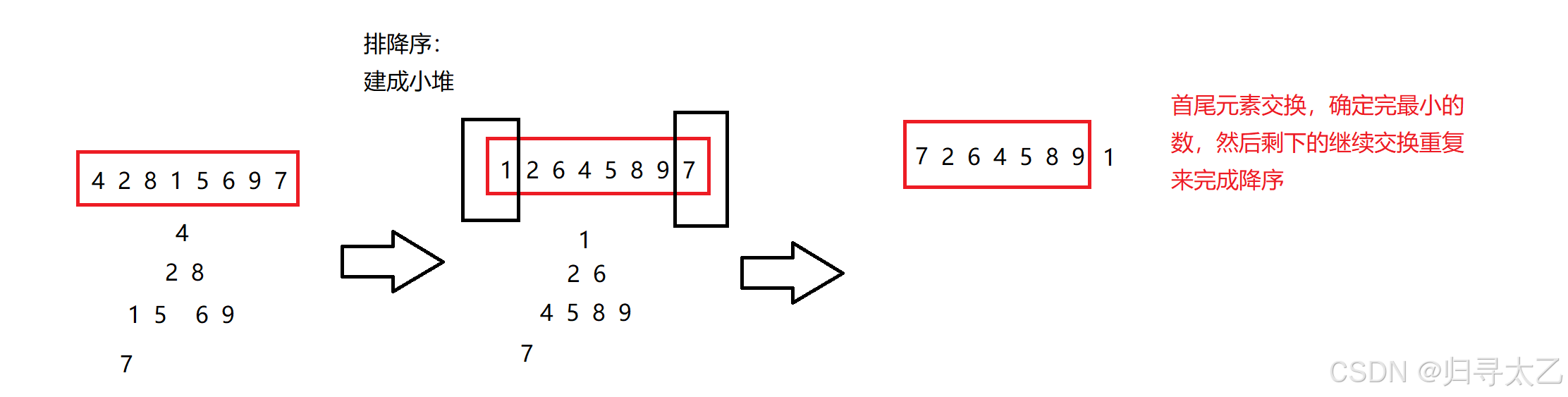
写成代码:
{int arr[] = { 1,43,23,4,575,68,34,7,5,24,3,13,54, };int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){AdjustUp(arr, i);}int end = n - 1;while (end > 0){Swap(&arr[0], &arr[end]);AdjustDown(arr, end, 0);end--;}
}
这里我们通过调试,来观察结果:

2.3用向下调整来建堆
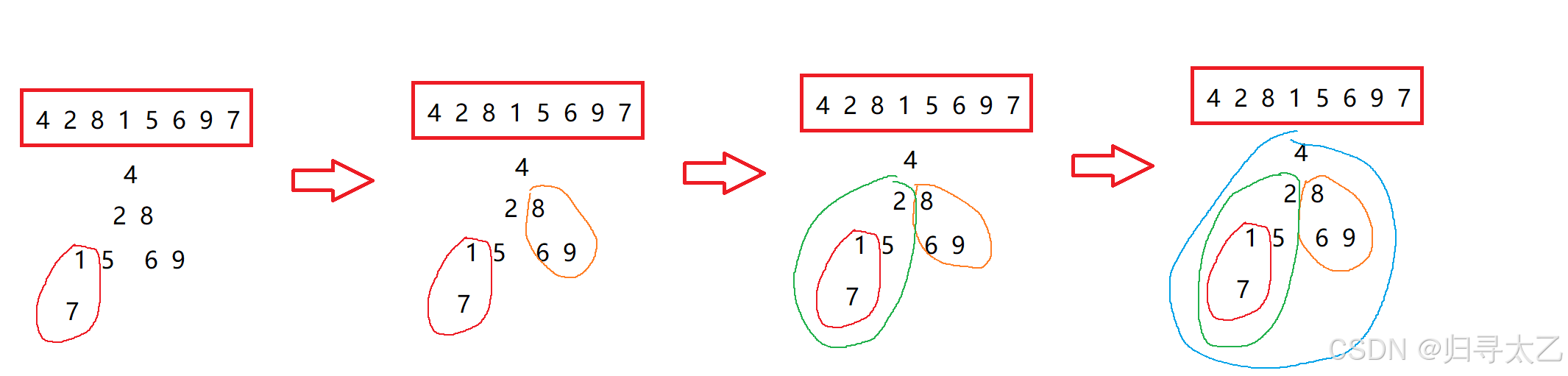
如果采用向下调整,我们就不能将数据从头开始遍历
通过直接找到最后的子叶来找到他的父亲
接着调整这一棵以他父亲为根的小树
然后去找他父亲前面的数据
接着重复遍历,最后完成整棵树的遍历
void Test03()
{int arr[] = { 1,43,23,4,575,68,34,7,5,24,3,13,54, };int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);int end = n - 1;int parent = (end - 1) / 2;for (int i = parent; i >= 0; i--){AdjustDown(arr, n, i);}while (end > 0){Swap(&arr[0], &arr[end]);AdjustDown(arr, end, 0);end--;}
}
3.建堆的时间复杂度的计算
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent)
{int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < n){//用假设法判断哪个孩子较小if (a[child] > a[child + 1] && child + 1 < n){child = child + 1;}if (a[child] < a[parent]){Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{break;}}
}void Test03()
{int arr[] = { 1,43,23,4,575,68,34,7,5,24,3,13,54, };int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);int end = n - 1;int parent = (end - 1) / 2;for (int i = parent; i >= 0; i--){AdjustDown(arr, n, i);}
}
这段代码的时间复杂度如何计算的:
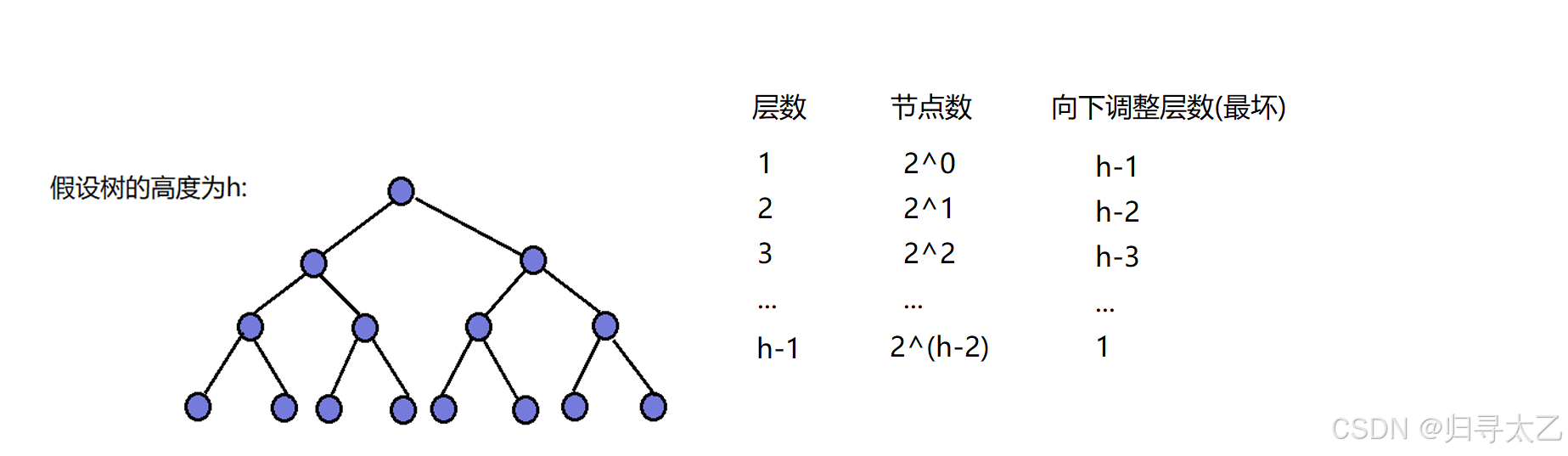
可以算出总步数:
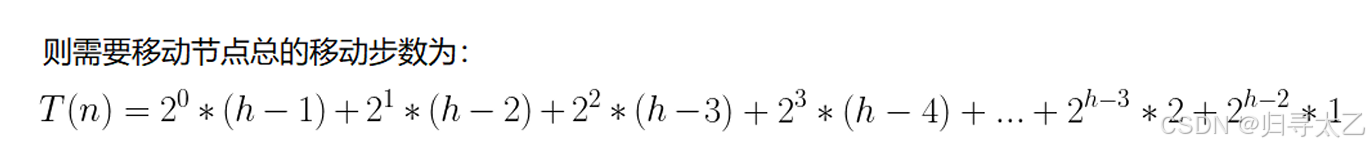
这里通过数学关系(错位相减法):
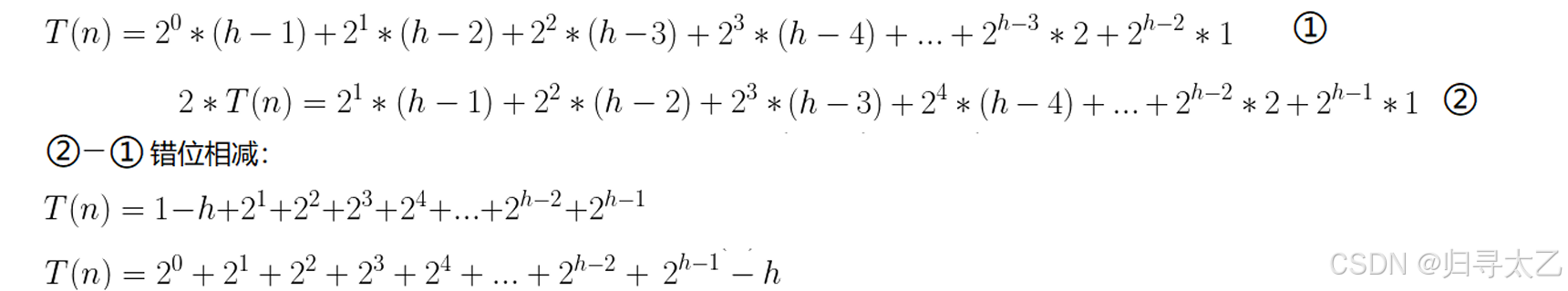
再通过等比数列求和公式:
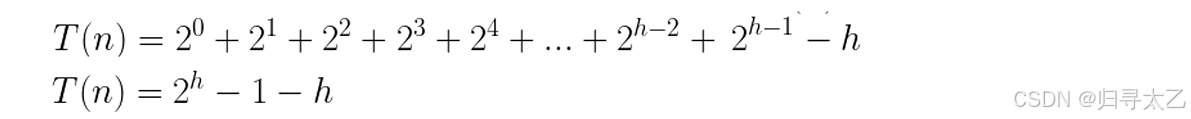
接着我们可以找到节点总数和高度的关系
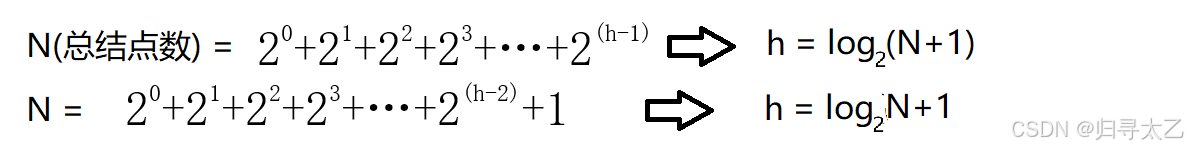
我们这里看成是最多的,带入计算:
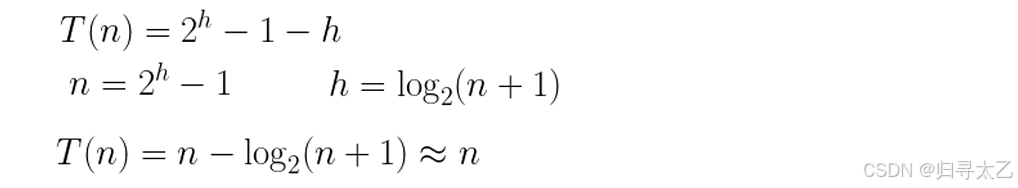
所以这个函数的时间复杂度是O=(N)
4.TOP-K问题
TOP-K问题:即求数据结合中前K个最大的元素或者最小的元素,一般情况下数据量都比较大。
比如:专业前10名、世界500强、富豪榜、游戏中前100的活跃玩家等。
-
方法一:
将这n个数建成一个大堆,不断通过pop和top来找到最大的数
缺点,如果n过大所需的空间也就很大
例如:如果数据为10亿则需要消耗4G左右的空间
可以改进为每次仅提取前20%的数据,然后找到最大的10个数
最后找完总共50个数再对这50个数再进行pop,top
但如果空间还是不够,则就不采取这种方法了因为这种方法本质上就是拿空间换时间,如果分的再小一些就无法以空间换时间了 -
方法二:
用前k个数建成小堆,对剩下的数与堆顶的数比较大的就进堆
再将堆进行向下调整
使较大的数沉底,然后不断比较取到前k个数
写成代码:
void CreateNDate()
{// 造数据int n = 100000;srand(time(0));const char* file = "data.txt";FILE* fin = fopen(file, "w");if (fin == NULL){perror("fopen error");return;}for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){int x = (rand()+i);fprintf(fin, "%d\n", x);}fclose(fin);
}void TestHeap3()
{int k;printf("请输入k>:");scanf("%d", &k);int* kminheap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);if (kminheap == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}const char* file = "data.txt";FILE* fout = fopen(file, "r");if (fout == NULL){perror("fopen error");return;}// 读取文件中前k个数for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fscanf(fout, "%d", &kminheap[i]);}// 建K个数的小堆for (int i = (k-1-1)/2; i>=0 ; i--){AdjustDown(kminheap, k, i);}// 读取剩下的N-K个数int x = 0;while (fscanf(fout, "%d", &x) > 0){if (x > kminheap[0]){kminheap[0] = x;AdjustDown(kminheap, k, 0);}}printf("最大前%d个数:", k);for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){printf("%d ", kminheap[i]);}printf("\n");
}






