09-new and delete
dynamic memory allocation 在堆里面申请空间
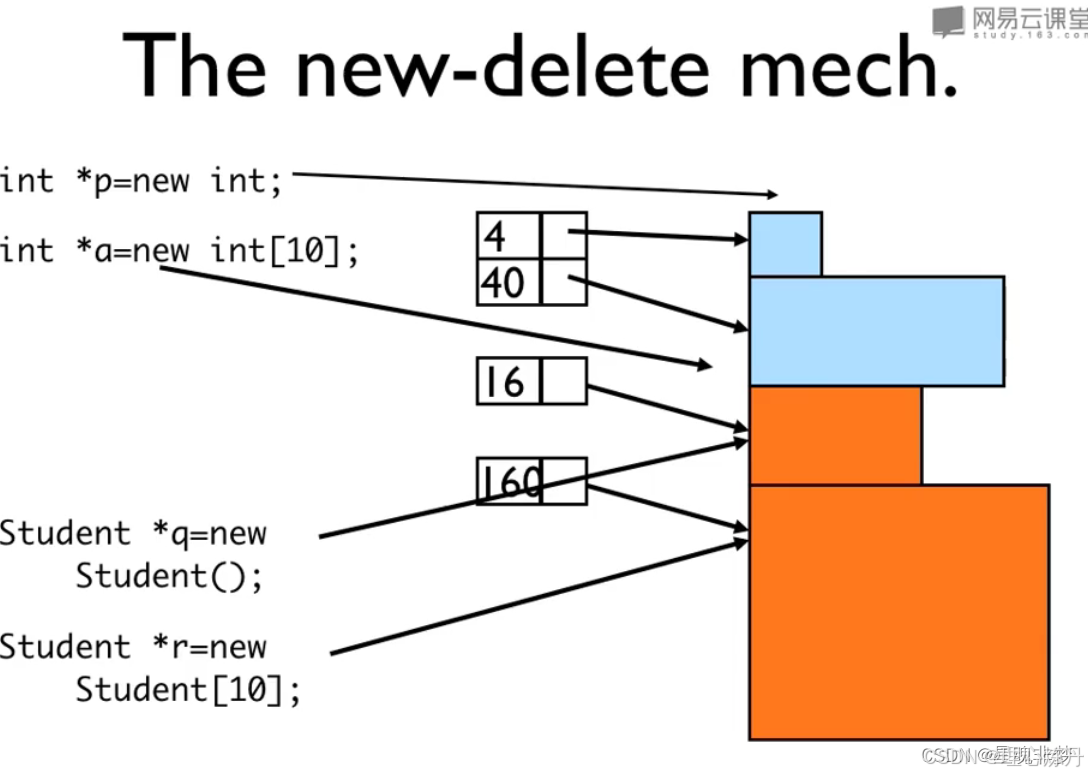
new
- new int; // 分配一块 int 空间
- new Stash; // 分配Stash对象的空间 然后调用构造函数初始化
- new int[10] // 分配10个int 空间
delete // 给它一个地址
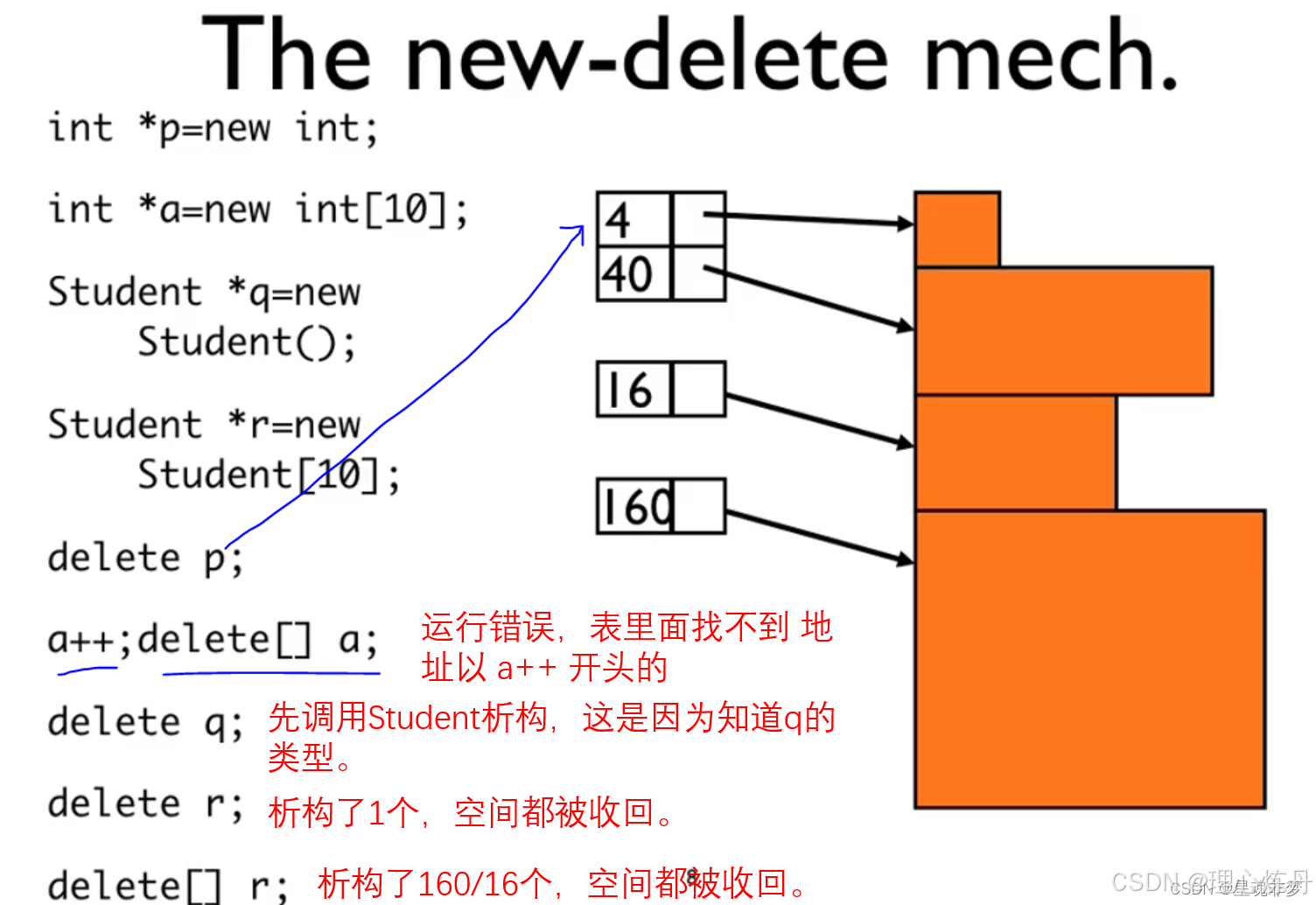
- delete p; //
- delete[] p;
相当于c中malloce和free
任何运算都有结果,new操作返回的是地址
动态制造对象。 new 带着[ ], delete 也要带着[]。
delete p所指的对象时候,析构函数先被调用,然后空间被回收。
new and delete
- new is the way to allocate memory as a program runs. Pointers become the only access to that memory
- delete enables you to return memory to the memory pool when you are finished with it
dynamic arrays
int * psome = new int [10]; // 动态申请数组
- the new operator returns the address of the first element of the block
delete [] psome; // []释放,10个析构都会被调用, 不带[]只有一个被析构
- the presence of the brackets tells the program that it should free the whole array,not just the element
tips for new an delete
- don’t use delete to free memory that new didn’t allocate
- don’t use delete to free the same block of memory twice in succession(连续)
- use delete[] if you used new [] to allocate an array
- use delete (no brackets) if you used new to allocate an array
- it’s safe to apply delete to the null pointer (noting happens)

new了对象但是不delete,因为我们现在的程序都是跑一下,我们的操作系统都是多进程,程序每次运行都是一个进程,操作系统给分配了虚拟空间,当程序结束后,空间会被回收,即使申请了内存没有释放,打开文件没有关闭,但是程序结束后都结束了。
但是如果程序要一直运行,那么会存在内存泄漏问题。
10-访问限制
setting limits
- to keep the client programmer’s hands off members they shouldn’t touch
- to allow the library designer to change the internal working of the structure without worrying about how it will affect the client programmer
C++ access control
- the members of a class can be cataloged,marked as:
- public
- private
- protected
public公开的。所有的都可以访问
private私有的。类的成员函数可以访问这些私有的成员函数或者成员变量;
private是对类来说的不是对对象来说的,同一个类的对象是可以互相访问私有变量的,private的这种限制仅仅是在编译时刻,运行时刻仍然有办法访问别的类的私有成员protected。类自己以及子子孙孙可以访问
public
- public means all member declarations that follow are available to everyone
private
- the private keyword means that no one can access that member except inside function members of that type
自己指的是这个类的成员函数。
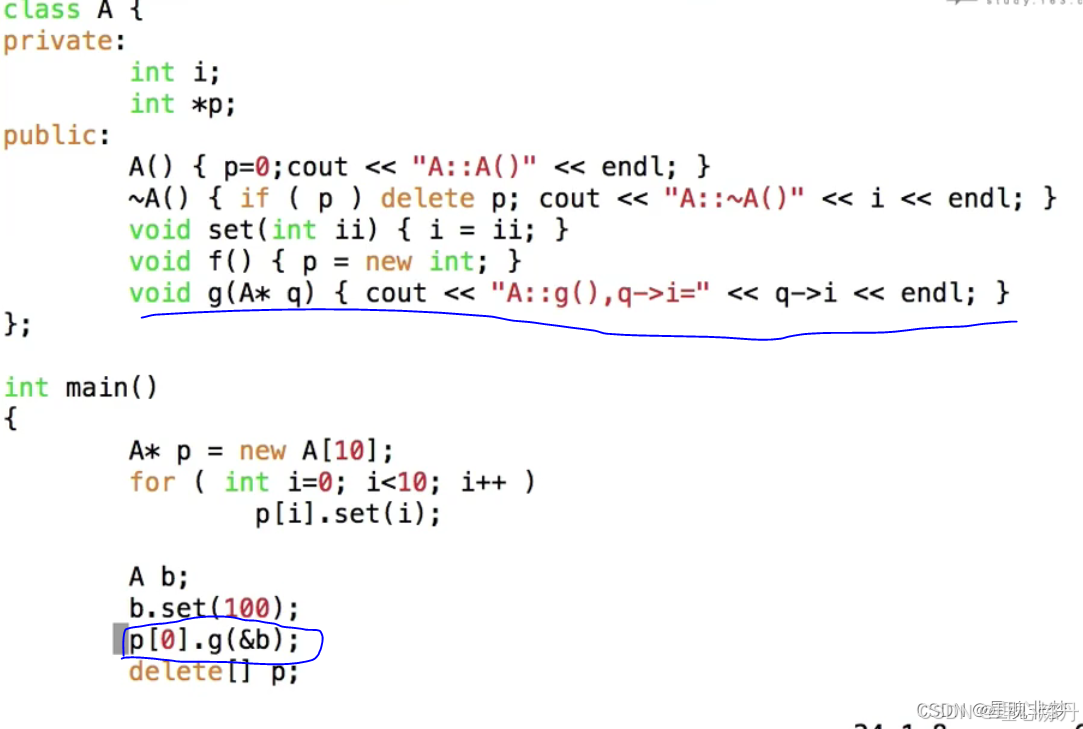
private是对类来说的,不是对对象的。同一个类的对象之间是可以互相访问私有的成员变量的。private的限制仅仅在编译时刻,意味着,运行时刻可以访问私有的东西。C++的OOP 仅在源代码时候存在,编译后的 .o 和其他语言是一样的,不会在运行时刻检查访问限制。
friends
- to explicitly grant access to a function that isn’t member of the structure
- the class itself controls which code has access to its members
- can declare a global function as a friend, as well as a member function of another class,or even an entire class,as a friend
别的类,别的函数,别的类内的某个函数
friend的授权也是在编译时刻检查的。运算符重载时候用的较多。
class vs. struct
- class defaults to private
- struct defaults to public







