

目录
- 项目背景
- 技术栈和项目环境
- 正排索引和倒排索引
- 数据去标签与清洗
- 下载数据源
- 去标签
- 建立索引
- 构建正排索引
- 构建倒排索引
- 建立搜索引擎
- http_server 服务
- 搜索到的内容有重复
文章末有源码链接。
项目背景
目前我们常用的搜索引擎有Google、百度、360等,这些搜索引擎都是超大型超完善的全网搜索,而本项目Boost搜索引擎只是一个非常简单的站内搜索。
| 比较维度 | 全网搜索 | 站内搜索 |
|---|---|---|
| 搜索范围与数据来源 | 覆盖整个互联网,数据来源广泛,需搜索引擎爬虫抓取收录网页 | 限定在特定网站内部,数据仅来源于该网站自身内容 |
| 搜索效率 | 范围广、数据量大,检索复杂,速度相对较慢,结果筛选耗时 | 搜索范围小,速度更快,可快速定位信息 |
| 可控性 | 用户和网站管理者无法干涉搜索引擎算法,搜索结果不可控 | 网站管理者可优化搜索功能,根据需求调整搜索算法等,具有可控性 |
| 索引构建 | 需构建庞大复杂的索引系统处理海量数据,技术难度高 | 针对特定网站内容和数据结构优化,索引构建相对简单且更具针对性 |
为什么选做Boost的搜索引擎呢?
作为C++选手,相信大家都浏览过Boost官网,而我们在2023年之前浏览Boost官网时是没有搜索功能的,虽然自从2023年起新增了搜索功能,但这之前给我们的不太好的浏览体验可能还是耿耿于怀,所以本项目选做Boost搜索引擎,算是弥补之前没有的遗憾吧(虽然肯定没有现在官网提供的好用🤡)。
我们最熟悉最常用的站内搜索cplusplus官网,当我们想查看 vector 的官方文档时可以直接在搜索框中搜索,就能得到我们想要的信息。

虽然我们无法独立实现向百度这样大型的搜索引擎,但是通过本项目Boost搜索引擎这个站内搜索小项目,可以做到管中窥豹的效果,大致了解像他们这样大型的工程整体框架是什么样的,是怎么运作的。
首先我们来看看百度搜索是以什么样的方式展示的:

可以看到基本有这三部分内容,(当然还有图片,为了简单我们就不展示图片了😜)那本项目也就模仿这样的格式展示搜索到的结果。
另外,当我们的搜索语句中有多个搜索关键词的时候,它是不严格匹配的,因此我们需要有一个切分搜索关键字的过程。这个任务可以借助 cppjieba 这个库来帮我们完成。



搜索引擎的宏观原理:
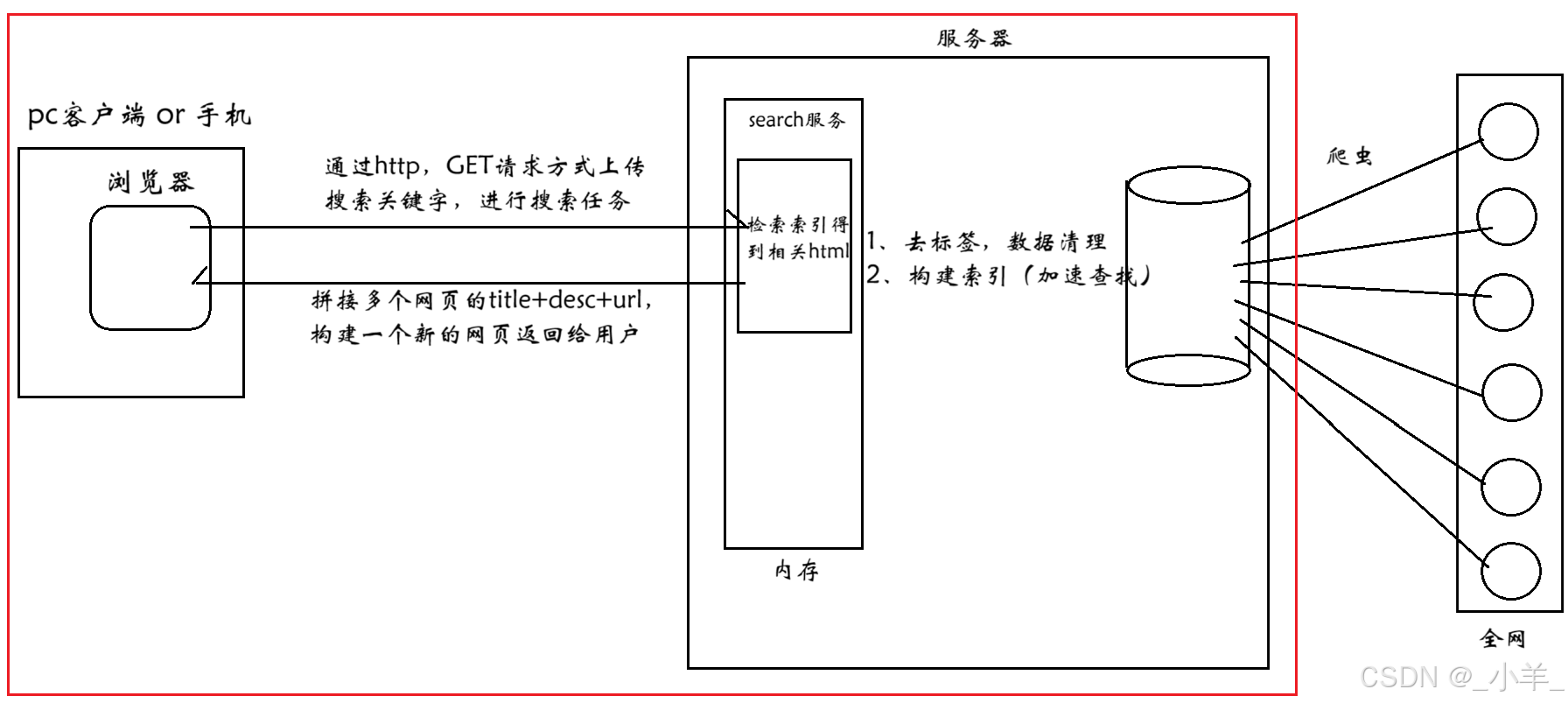
本项目实现的是红色框框中的内容。
技术栈和项目环境
- 技术栈:C/C++、C++11、STL、Boost库、JsonCpp、cppjieba、cpp-httplib;
- 项目环境:Ubuntu-22.04、vscode、gcc/g++、makefile。
cppjieba是一个用 C++ 实现的中文分词库,它具有高效、准确、易用等特点;cpp-httplib是一个轻量级、跨平台的 C++ HTTP 库,它以单头文件的形式存在,使用起来非常便捷。
正排索引和倒排索引
首先我们通过一个例子来了解下什么是正排和倒排索引:
- 文档1:小帅是安徽理工大学的三好学生
- 文档2:小帅是安徽理工大学电信院的学生会主席
正排索引:从文档ID找到文档内容(文档中的关键字)。
| 文档ID | 文档内容 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 小帅是安徽理工大学的三好学生 |
| 2 | 小帅是安徽理工大学电信院的学生会主席 |
目标文档进行分词(方便建立倒排索引和查找):
- 文档1:小帅、安徽理工大学、三好学生、学生
- 文档2:小帅、安徽理工大学、电信院、学生、学生会、主席
倒排索引:根据文档内容分词,整理不重复的关键字,找到对应文档ID的方案。
| 关键字 | 文档ID |
|---|---|
| 小帅 | 文档1、文档2 |
| 安徽理工大学 | 文档1、文档2 |
| 三好学生 | 文档1 |
| 学生 | 文档1、文档2 |
| 电信院 | 文档2 |
| 学生会 | 文档2 |
| 主席 | 文档2 |
当用户输入学生:倒排索引中查找 -> 提取文档ID -> 根据正排索引 -> 找到文档内容 ->
title+desc+url -> 构建响应结果。
文档1和文档2中都有学生这个关键字,那先显示谁呢?我们后面在搭建的时候会给每个文档设置权重。
数据去标签与清洗
下载数据源
首先从Boost官网下载数据源:

下载好后通过 rz -E 拉取到Ubuntu服务器上,然后 tar xzf 解压,我们只需要 boost_1_88_0\doc\html 中的内容,将所有内容拷贝到新目录中,其他的部分就可以删除掉了,得到下面这些文件:

把每个html文件名和路径保存起来,方便后续文件读取:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <boost/filesystem.hpp>const std::string src_path = "data/input/";
const std::string output = "data/raw_html/raw.txt";// 文档格式
typedef struct DocInfo
{std::string title; std::string content;std::string url;
}DocInfo_t;bool EnumFile(const std::string &src_path, std::vector<std::string> *files_list)
{namespace fs = boost::filesystem;fs::path root_path(src_path);if (fs::exists(root_path) == false) // 判断路径是否存在{std::cerr << src_path << " not exists" << std::endl;return false;}fs::recursive_directory_iterator end;for (fs::recursive_directory_iterator it(root_path); it != end; it++){if (fs::is_regular_file(*it) == false) // 判断是否是普通文件{continue;}if (it->path().extension() != ".html") // 判断文件路径名是否符合要求{continue;}std::cout << "debug: " << it->path().string() << std::endl;files_list->push_back(it->path().string());}return true;
}bool ParseHtml(const std::vector<std::string> &files, std::vector<DocInfo_t> *results)
{return true;
}bool SaveHtml(const std::vector<DocInfo_t> &results, const std::string &output)
{return true;
}int main()
{// 1.把每个html文件名和路径保存起来,方便后续文件读取std::vector<std::string> files_list;if (EnumFile(src_path, &files_list) == false){std::cerr << "enum file name fail!" << std::endl;return 1;}// 2.按照files_list读取每个文件的内容,并进行解析std::vector<DocInfo_t> results;if (ParseHtml(files_list, &results) == false){std::cerr << "parse html fail!" << std::endl;return 2;}// 3.把解析完毕的各个文件内容写入到output中,按照 \3 作为每个文档的分隔符if (SaveHtml(results, output) == false){std::cerr << "save html fail!" << std::endl;return 3;}return 0;
}
Boost库不是C++标准库,因此在编写makefile时别忘了链接指定库哦:
cc=g++parser : parser.cc$(cc) -o $@ $^ -lboost_system -lboost_filesystem -std=c++11.PHONY:clean
clean:rm -f parser
通过打印调式,我们就能得到下面这些信息:

去标签
什么是标签?我们随便打开一个上面的文件:

- 标签对我们搜索是没有价值的,因此需要去掉这些标签,剩下的内容就是我们需要的;
- 我们的目标是把每个文档都去标签,然后把内容写入到同一个文件中,每个文档内容不需要任何换行,文档和文档之间用
\3区分,这样做是为了读取的时候更方便; - 比如:
title\3content\3url \n title\3content\3url...,用getline(ifstream, line)直接读取一个文档的全部内容,然后再根据 \3 获取各个部分。
按照files_list读取每个文件的内容,并进行解析:
bool ParseHtml(const std::vector<std::string> &files_list, std::vector<DocInfo_t> *results)
{for (const std::string &file : files_list){std::string result;if (yjz_util::FileUtil::ReadFile(file, &result) == false) continue;DocInfo_t doc;if (ParseTitle(result, &doc.title) == false) continue;if (ParseContent(result, &doc.content) == false) continue;if (ParseUrl(file, &doc.url) == false) continue;results->push_back(std::move(doc));}return true;
}
提取title:

static bool ParseTitle(const std::string &file, std::string *title)
{size_t begin = file.find("<title>");if (begin == std::string::npos) return false;size_t end = file.find("</title>");if (end == std::string::npos) return false;begin += std::string("<title>").size();if (begin > end) return false;*title = file.substr(begin, end - begin);return true;
}
提取content,也就是去标签,我们只需要像下面这种白色的内容:

static bool ParseContent(const std::string &file, std::string *content)
{// 状态机enum status{LABLE,CONTENT};enum status s = LABLE; // 开始默认为标签for (char c : file){switch (s){case LABLE : if (c == '>') s = CONTENT; break; // 如果遇到'>',假设接下来是contentcase CONTENT : if (c == '<') s = LABLE; // 如果假设错误,状态重新转为lableelse{// 后面我们想用\n作为html解析后文本的分隔符if (c == '\n') c = ' ';content->push_back(c);}break;default : break;}}return true;
}
构建URL:

static bool ParseUrl(const std::string &file_path, std::string *url)
{std::string url_head = "https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_88_0/doc/html";std::string url_tail = file_path.substr(src_path.size());*url = url_head + url_tail;return true;
}
将解析的内容写入到指定的文件中:
bool SaveHtml(const std::vector<DocInfo_t> &results, const std::string &output)
{
#define SEP '\3'// 按二进制方式写入std::ofstream out(output, std::ios::out | std::ios::binary);if (out.is_open() == false){std::cerr << "open " << output << " fail!" << std::endl;return false;}for (auto &it : results){std::string out_string;out_string = it.title;out_string += SEP;out_string += it.content;out_string += SEP;out_string += it.url;out_string += '\n';out.write(out_string.c_str(), out_string.size());}out.close();return true;
}
建立索引
index.hpp 的基本结构:
namespace yjz_index
{struct DocInfo{std::string title;std::string content;std::string url;uint64_t doc_id;};struct InvertedElem{uint64_t doc_id; // 文档IDstd::string word; // 关键字int weight; // 权重};class Index{private:Index(){}Index(const Index&) = delete;Index& operator=(const Index&) = delete;static Index *_instance;static std::mutex _mutex;public:using InvertedList = std::vector<InvertedElem>;~Index(){}// 获取单例static Index* GetInstance(){}// 根据文档ID找到文档内容DocInfo* GetForwardIndex(uint64_t doc_id){}// 根据关键字找到倒排拉链InvertedList* GetInvertedList(const std::string &word){}// 根据格式化后的文档,构建正排、倒排索引bool BuildIndex(const std::string &input){}private:// 构建正排索引DocInfo* BuildForwardIndex(const std::string &line){}// 构建倒排索引bool BuildInvertedIndex(const DocInfo &doc){}private:// 将数组下标作为文档IDstd::vector<DocInfo> _forward_index; // 正排索引std::unordered_map<std::string, InvertedList> _inverted_index;};Index* Index::_instance= nullptr;std::mutex Index::_mutex;
}
构建正排索引
将符合特定格式的字符串解析并转化为结构化的文档信息对象,进而添加到正排索引数据结构(_forward_index 容器 )中,为后续基于文档信息的检索、分析等操作提供基础。
DocInfo* BuildForwardIndex(const std::string &line)
{// 解析line,字符串切分std::vector<std::string> results;const std::string sep = "\3";yjz_util::StringUtil::Split(line, &results, sep);if (results.size() != 3){return nullptr;}// 将切分好的字符串构建DocInfoDocInfo doc;doc.title = results[0];doc.content = results[1];doc.url = results[2];doc.doc_id = _forward_index.size(); // 先更新文档ID再插入_forward_index.push_back(std::move(doc));return &_forward_index.back();
}
构建倒排索引
对给定的文档进行分词处理,统计每个单词在标题和内容中的出现次数,计算每个单词的权重,然后将这些信息添加到倒排索引中。通过这种方式,可以快速查找包含特定单词的文档,并根据单词的权重对文档进行排序。
// 构建倒排索引
bool BuildInvertedIndex(const DocInfo &doc)
{// doc -> 倒排拉链struct word_cnt{int title_cnt;int content_cnt;word_cnt() : title_cnt(0), content_cnt(0) {}}; std::unordered_map<std::string, word_cnt> word_map; // 暂存词频std::vector<std::string> title_words;yjz_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(doc.title, &title_words);for (auto &s : title_words){boost::to_lower(s); // 全部转化为小写word_map[s].title_cnt++;}std::vector<std::string> content_words;yjz_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(doc.content, &content_words);for (auto &s : content_words){boost::to_lower(s); word_map[s].content_cnt++;}for (auto &word_pair : word_map){InvertedElem item;item.doc_id = doc.doc_id;item.word = word_pair.first;item.weight = 10 * word_pair.second.title_cnt + word_pair.second.content_cnt;InvertedList &inverted_list = _inverted_index[word_pair.first];inverted_list.push_back(std::move(item));}return true;
}
Boost库切分字符串:
static void CutString(const std::string &line, std::vector<std::string> *result, const std::string &sep)
{boost::split(*result, line, boost::is_any_of(sep), boost::token_compress_on);
}
boost::split函数:这是 Boost 库中的一个函数,用于将字符串按照指定的分隔符进行分割;*result:通过解引用指针 result,将分割后的子字符串存储到该向量中;line:待分割的输入字符串;boost::is_any_of(sep):用于指定分割字符串时使用的分隔符;boost::token_compress_on:这是一个分割标志,设置为 boost::token_compress_on 表示如果连续出现多个分隔符,会将它们视为一个分隔符进行处理,避免产生空的子字符串。
建立搜索引擎
searcher.hpp 基本框架:
namespace yjz_searcher
{class Searcher{public:Searcher(){}~Searcher(){}struct InvertedElemPrint{uint64_t doc_id;int weight;std::vector<std::string> words; // 多个词对应同一个doc_idInvertedElemPrint() : doc_id(0), weight(0) {}};void InitSearcher(const std::string &input){// 获取或创建index对象_index = yjz_index::Index::GetInstance();std::cout << "获取或创建index单例成功!" << std::endl;_index->BuildIndex(input);std::cout << "建立正排和倒排索引成功!" << std::endl;}void Search(const std::string &query, std::string *json_string){// 1.分词,对query(搜索关键字)按要求进行分词// 2.触发,根据分好的词进行索引查找,关键字需要忽略大小写// 3.合并排序,汇总查找结果,按照权重排降序// 4.根据查找出来的结果,构建Json串}// 获取摘要std::string GetDesc(const std::string &html_content, const std::string &word){}private:yjz_index::Index *_index; };
}
编写Search函数:
void Search(const std::string &query, std::string *json_string)
{// 1.分词,对query(搜索关键字)按要求进行分词std::vector<std::string> words;yjz_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(query, &words);// 2.触发,根据分好的词进行索引查找,关键字需要忽略大小写yjz_index::Index::InvertedList inverted_list_all;for (auto word : words){boost::to_lower(word);yjz_index::Index::InvertedList *inverted_list = _index->GetInvertedList(word);if (inverted_list == nullptr) continue;inverted_list_all.insert(inverted_list_all.end(), inverted_list->begin(), inverted_list->end());}// 3.合并排序,汇总查找结果,按照权重排降序std::sort(inverted_list_all.begin(), inverted_list_all.end(), [](const yjz_index::InvertedElem& e1, const yjz_index::InvertedElem& e2){return e1.weight > e2.weight;});// 4.根据查找出来的结果,构建Json串Json::Value root;for (auto &it : inverted_list_all){// 根据文档ID进行正排索引yjz_index::DocInfo *doc = _index->GetForwardIndex(it.doc_id); if (doc == nullptr) continue;Json::Value elem;elem["title"] = doc->title;elem["desc"] = GetDesc(doc->content, it.word);elem["url"] = doc->url;// for Debug// elem["id"] = it.doc_id;// elem["weight"] = it.weight;root.append(elem);}Json::StyledWriter writer;*json_string = writer.write(root);
}
获取摘要:找到word关键字在html_content中首次出现的位置,规定往前找50字节,往后找100字节,截取这部分内容。
因为我们在构建倒排索引和索引查找时将关键字统一转换为了小写,因此在原始数据中查找时也应该统一按小写字母查找。
search函数定义在<algorithm>头文件中,用于在一个序列中查找另一个序列首次出现的位置,并支持自定义查找规则。
std::string GetDesc(const std::string &html_content, const std::string &word)
{const int pre_step = 50;const int next_step = 100;// 找到首次出现auto it = std::search(html_content.begin(), html_content.end(), word.begin(), word.end(), [](char x, char y){return std::tolower(x) == std::tolower(y);});if (it == html_content.end()) return "None1";int pos = std::distance(html_content.begin(), it);int start = 0;int end = html_content.size() - 1;start = std::max(start, pos - pre_step);end = std::min(end, pos + next_step);if (start >= end) return "None2";return html_content.substr(start, end - start);
}
我们想知道现在的搜索结果是不是按照我们预想的按照权重 weight 进行顺序呈现的呢?
在 search 函数中构建Json串时,我们把文档ID和权重加上进行测试:

下面是搜索结果:


可以看到是没有问题的。
http_server 服务
下载 cpp-httplib 库,然后直接参照给的示例编写我们想要的服务,非常简单。
#include "cpp-httplib/httplib.h"
#include "searcher.hpp"const std::string input = "data/raw_html/raw.txt";
const std::string root_path = "./wwwroot";int main()
{yjz_searcher::Searcher search;search.InitSearcher(input);httplib::Server svr;svr.set_base_dir(root_path);svr.Get("/s", [&search](const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &rsp){if (req.has_param("word") == false) {rsp.set_content("必须要有搜索关键字!", "text/plain: charset=utf-8");return;}std::string word = req.get_param_value("word");std::cout << "用户在搜索: " << word << std::endl;std::string json_string;search.Search(word, &json_string);rsp.set_content(json_string, "application/json");});svr.listen("0.0.0.0", 8081);return 0;
}
当然我们也可以自己搭建http服务。
到这里后端的工作基本已经完成了,那前端代码怎么办呢?我这里就直接让Deepseek帮我写了,如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no"><script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script><link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/6.0.0/css/all.min.css"><title>Boost 智能搜索引擎</title><style>:root {--primary-color: #4e6ef2;--hover-color: #3b5bdb;--background: #f8f9fa;--text-dark: #2d3436;--text-light: #636e72;}* {margin: 0;padding: 0;box-sizing: border-box;font-family: 'Segoe UI', system-ui, sans-serif;}body {background: var(--background);min-height: 100vh;padding: 2rem 1rem;}.container {max-width: 800px;margin: 0 auto;animation: fadeIn 0.5s ease;}.search-box {display: flex;gap: 10px;margin-bottom: 2rem;box-shadow: 0 4px 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);border-radius: 30px;background: white;padding: 5px;}.search-input {flex: 1;padding: 1rem 1.5rem;border: none;border-radius: 30px;font-size: 1.1rem;color: var(--text-dark);transition: all 0.3s ease;}.search-input:focus {outline: none;box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px rgba(78, 110, 242, 0.2);}.search-btn {padding: 0 2rem;border: none;border-radius: 30px;background: linear-gradient(135deg, var(--primary-color), var(--hover-color));color: white;font-size: 1rem;font-weight: 600;cursor: pointer;transition: all 0.3s ease;display: flex;align-items: center;gap: 8px;}.search-btn:hover {background: var(--hover-color);transform: translateY(-1px);}.result-item {background: white;border-radius: 12px;padding: 1.5rem;margin-bottom: 1rem;box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);transition: transform 0.2s ease;}.result-item:hover {transform: translateX(5px);}.result-title {color: var(--primary-color);font-size: 1.2rem;font-weight: 600;margin-bottom: 0.5rem;text-decoration: none;display: flex;align-items: center;gap: 8px;}.result-title:hover {text-decoration: underline;}.result-desc {color: var(--text-dark);line-height: 1.6;margin-bottom: 0.5rem;display: -webkit-box;-webkit-line-clamp: 3;-webkit-box-orient: vertical;overflow: hidden;}.result-url {color: var(--text-light);font-size: 0.9rem;font-family: monospace;}.loading {text-align: center;padding: 2rem;color: var(--text-light);}@keyframes fadeIn {from { opacity: 0; transform: translateY(20px); }to { opacity: 1; transform: translateY(0); }}@media (max-width: 768px) {.search-box {flex-direction: column;border-radius: 15px;}.search-btn {padding: 1rem;justify-content: center;}}</style>
</head>
<body><div class="container"><div class="search-box"><input type="text" class="search-input" placeholder="请输入搜索关键词..." autofocus><button class="search-btn" onclick="search()"><i class="fas fa-search"></i>搜索</button></div><div class="result-container"></div></div><script>// 增强功能$(document).ready(() => {// 回车键搜索$('.search-input').keypress(e => e.which === 13 && search())// 输入框交互$('.search-input').focus(function() {if (this.value === "请输入搜索关键词...") this.value = ""}).blur(function() {if (this.value === "") this.value = "请输入搜索关键词..."})})function search() {const query = $('.search-input').val().trim()if (!query) return// 显示加载状态$('.result-container').html(`<div class="loading"><i class="fas fa-spinner fa-spin"></i>正在搜索中...</div>`)$.ajax({url: `/s?word=${encodeURIComponent(query)}`,method: 'GET',success: buildResults,error: () => {$('.result-container').html(`<div class="result-item" style="color: #dc3545;"><i class="fas fa-exclamation-triangle"></i>请求失败,请稍后重试</div>`)}})}function buildResults(data) {const container = $('.result-container').empty()if (data.length === 0) {container.html(`<div class="result-item"><div style="color: var(--text-light); text-align: center;"><i class="fas fa-search-minus"></i>没有找到相关结果</div></div>`)return}data.forEach(item => {const elem = $(`<div class="result-item"><a href="${item.url}" class="result-title" target="_blank"><i class="fas fa-link"></i>${item.title}</a><p class="result-desc">${item.desc}</p><div class="result-url">${item.url}</div></div>`)container.append(elem)})}</script>
</body>
</html>
最后结果展示:

可以看到非常完美,Deepseek写的页面还是非常好看的。
但是目前的代码还有一个不易察觉的问题,当我们输入搜索内容,通过 cppjieba 分词得到多个关键词,这些关键词可能都来自同一个文档,根据目前的代码每个关键词都会通过索引查找到这个文档,也就是说这个文档会给我们呈现多份,而我们希望得到的只是一个文档就行,因此接下来还需要优化一下去重的问题。
搜索到的内容有重复
下面是一个测试文件:


可以看到通过 cppjieba 分词然后通过每个关键词都索引到了这个文档,给我们重复呈现了四次。
接下来考虑如何去重。我们可以根据一个文档只有一个 doc_id 的特点,将所有 doc_id 相同的关键词统计到一起,权重累加。
struct InvertedElemPrint
{uint64_t doc_id;int weight;std::vector<std::string> words; // 多个词对应同一个doc_idInvertedElemPrint() : doc_id(0), weight(0) {}
};
//... void Search(const std::string &query, std::string *json_string)
{// 1.分词,对query(搜索关键字)按要求进行分词std::vector<std::string> words;yjz_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(query, &words);// 2.触发,根据分好的词进行索引查找,关键字需要忽略大小写// yjz_index::Index::InvertedList inverted_list_all;std::unordered_map<uint64_t, InvertedElemPrint> tokens_map; // 通过doc_id去重for (auto word : words){boost::to_lower(word);yjz_index::Index::InvertedList *inverted_list = _index->GetInvertedList(word);if (inverted_list == nullptr) continue;//inverted_list_all.insert(inverted_list_all.end(), inverted_list->begin(), inverted_list->end());for (const auto &elem : *inverted_list){auto &item = tokens_map[elem.doc_id]; // 根据doc_id找到相同的索引节点item.doc_id = elem.doc_id;item.weight += elem.weight; // 权重累加item.words.push_back(elem.word); // 将相同doc_id的关键词管理到一起}}std::vector<InvertedElemPrint> inverted_list_all; // 保存不重复的倒排拉链节点for (const auto &item : tokens_map){inverted_list_all.push_back(std::move(item.second));}// 3.合并排序,汇总查找结果,按照权重排降序// std::sort(inverted_list_all.begin(), inverted_list_all.end(), // [](const yjz_index::InvertedElem& e1, const yjz_index::InvertedElem& e2){// return e1.weight > e2.weight;// });std::sort(inverted_list_all.begin(), inverted_list_all.end(), [](const InvertedElemPrint &e1, const InvertedElemPrint &e2){return e1.weight > e2.weight;});// 4.根据查找出来的结果,构建Json串Json::Value root;for (auto &it : inverted_list_all){// 根据文档ID进行正排索引yjz_index::DocInfo *doc = _index->GetForwardIndex(it.doc_id); if (doc == nullptr) continue;Json::Value elem;elem["title"] = doc->title;elem["desc"] = GetDesc(doc->content, it.words[0]);elem["url"] = doc->url;// for Debug// elem["id"] = it.doc_id;// elem["weight"] = it.weight;root.append(elem);}// Json::StyledWriter writer;Json::FastWriter writer;*json_string = writer.write(root);
}


完成去重结果。
最后我们可以通过下面的指令将服务放到后台运行,方便我们随时搜索。
nohup ./http_server &
Boost搜索引擎源码
本篇文章的分享就到这里了,如果您觉得在本文有所收获,还请留下您的三连支持哦~






